by M. Weisberger, January 7, 2020 in LiveScience
About 790,000 years ago, a meteor slammed into Earth with such force that the explosion blanketed about 10% of the planet with shiny black lumps of rocky debris. Known as tektites, these glassy blobs of melted terrestrial rock were strewn from Indochina to eastern Antarctica and from the Indian Ocean to the western Pacific. For more than a century, scientists searched for evidence of the impact that created these pitted blobs.
But the crater’s location eluded detection — until now.
Geochemical analysis and local gravity readings told researchers that the crater lay in southern Laos on the Bolaven Plateau; the ancient impact was concealed under a field of cooled volcanic lava spanning nearly 2,000 square miles (5,000 square kilometers), the scientists reported in a new study.
…
Was the crater buried? On Laos’ Bolaven Plateau, the scientists found a site where fields of volcanic lava might have hidden signs of an older meteor impact. In a region that the researchers targeted as a likely spot for a crater, most of the lava flows were also in the right age range: between 51,000 and 780,000 years old.
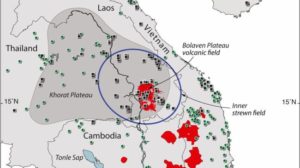
The study authors peered below the lava’s surface by taking gravity readings at more than 400 locations. Their resulting gravity map showed one area “of particular interest” with a gravitational anomaly, a subsurface zone less dense than the volcanic rock surrounding it. Their measurements hinted at an elliptical, “elongated crater” about 300 feet (100 m) thick, about 8 miles (13 km) wide and 11 miles (17 km) long, according to the study.
Together, all of these clues suggested that “this thick pile of volcanic rocks does indeed bury the site of the impact,” the scientists wrote.
The findings were published online Dec. 30 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
