by P Homewood, January 29, 2018 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
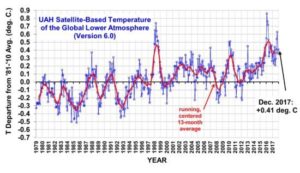
Using satellite data, a group of scientists has studied the development of temperature over the past 15 years in a large part of Greenland.
More precisely, they looked at surface temperatures (the temperature close to the Earth’s surface) in a part of the country that is not covered by ice—around one fifth of the surface area of Greenland.
Intuitively, you may think that temperature throughout all of Greenland has been increasing, but that is not the case. When you look at the yearly average, the ice-free parts of Greenland show a slight drop in temperature between 2001 and 2015. With swings in temperature from year to year.
However, these results should not be interpreted as “proof” that the Earth is not warming, say the scientists behind the research, which is published in the journal Scientific Reports.