by A. Watts, Aug 13, 2025 in WUWT
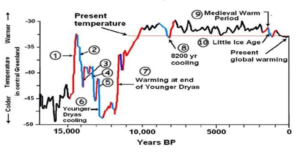
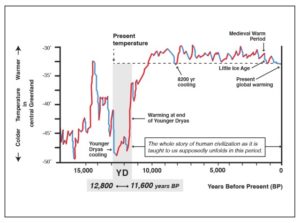
Northern Hemisphere cooling 12,800 years ago generally thought to be caused by glacial meltwater; new geochemical evidence might support comet impact.
Analysis of ocean sediments has surfaced geochemical clues in line with the possibility that an encounter with a disintegrating comet 12,800 years ago in the Northern Hemisphere triggered rapid cooling of Earth’s air and ocean. Christopher Moore of the University of South Carolina, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on August 6, 2025.
During the abrupt cool-off—the Younger Dryas event—temperatures dropped about 10 degrees Celsius in a year or less, with cooler temperatures lasting about 1,200 years. Many researchers believe that no comet was involved, and that glacial meltwater caused freshening of the Atlantic Ocean, significantly weakening currents that transport warm, tropical water northward. In contrast, the Younger Dryas Impact Hypothesis posits that Earth passed through debris from a disintegrating comet, with numerous impacts and shockwaves destabilizing ice sheets and causing massive meltwater flooding that shut down key ocean currents.
However, the impact hypothesis has been less well supported, lacking any evidence from ocean sediments. To address that gap, Moore and colleagues analyzed the geochemistry of four seafloor cores from Baffin Bay, near Greenland. Radiocarbon dating suggests the cores include sediments deposited when the Younger Dryas event began. To study them, the researchers used several techniques, including scanning electron microscopy, single-particle inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry, energy dispersive spectroscopy, and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry.
…