by Tom Kool, April 17, 2018 in Oilprice
Oil saw significant gains in anticipation of the strikes in Syria, but following U.S. efforts to ease geopolitical tensions in the region, crude prices have stabilized.
(…)
by Tom Kool, April 17, 2018 in Oilprice
Oil saw significant gains in anticipation of the strikes in Syria, but following U.S. efforts to ease geopolitical tensions in the region, crude prices have stabilized.
(…)
by Energy Voice, April 17, 2018 in GWPF
Chinese shale gas production will almost double between now and 2020, energy consultancy Wood Mackenzie (Woodmac) has predicted.
(…)
by P. Homewood, April 17, 2018 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
I was at the Mall last weekend, and came across this local anti fracking group holding some sort of a workshop.
One wonders if they realise where the energy they use every day comes from?
(…)
by Eric Worrall, April 13, 2018 in WUWT
h/t Geoff Sherrington – Coal is being rehabilitated as an essential component of the clean energy future.
Read more: http://www.abc.net.au/news/2018-04-12/coal-to-hydrogen-trial-for-latrobe-valley/9643570
Coal to hydrogen is not a new idea, the Water-gas shift reaction was discovered in 1780 by Italian Chemist Felice Fontana.
There are still some kinks to be worked out. The process to generate hydrogen from coal produces a monstrous amount of CO2 – far more CO2 per unit of useful energy than simply burning the coal would produce. But with hydrogen production, unlike hydrocarbon combustion, all the CO2 is produced in one place. This creates an opportunity for carbon sequestration, when technologies to sequester carbon on such an impressive scale are developed.
by Joe Ryan, April 12, 2018 in Bloomberg.News
(Bloomberg) — For all the buzz around wind, solar and electric cars, energy company executives had plenty to say Tuesday about the continuing role of fossil fuels and nuclear power at the Bloomberg New Energy Finance Future of Energy Summit.
Mining mogul Bob Murray offered a passionate defense of coal, asserting that we’d all “die in the dark” without it. Ethan Zindler, a Bloomberg New Energy Finance analyst, supplied the counter argument, saying U.S. coal-plant economics simply don’t work anymore. Here’s what executives from BP Plc to Tellurian Inc. said about the future of fossil fuels in a world pushing to fight climate change.
(…)
by Rick Wilkinson, April 12, 2018 in Oil&GasJournal
The New Zealand government has made the surprise announcement that it will not grant any new permits for offshore oil and gas exploration.
The Labor government of Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern said the move would not be retrospective. The country’s 22 existing offshore exploration permits along with any discoveries made in them could still lead to the granting of production licenses of up to 40 years duration.
by Connaissance des Energies, 24 octobre 2017
Dans cette note de synthèse en anglais, l’EIA américaine (Energy Information Administration), rappelle les grandes données énergétiques de l’Arabie saoudite qui a longtemps joué le rôle de « swing producer » sur le marché pétrolier, en faisant évoluer sa production et ses exportations selon l’offre et la demande mondiale de brut. Si le pays a perdu de son influence face à la révolution des hydrocarbures de roche-mère aux États-Unis, il constitue encore le membre central de l’OPEP, ayant joué un rôle moteur dans la décision de réduire la production des membres de cette organisation (d’autres producteurs comme la Russie s’étant associés à cet effort).
by Shane Hoover, April 4, 2018 in Inde.Online.com
Utica Midstream conference gives update on Utica Shale production and development.
NORTH CANTON Ohio has produced more natural gas than it uses since early 2015. Driven by prolific Utica Shale wells, the state produced a record 1.7 trillion cubic feet of natural gas last year.
Much of the regional economic development around that production has been in the form of pipelines and processing facilities.
Two interstate natural gas pipelines — Energy Transfer’s Rover project and the NEXUS Gas Transmission pipeline — cross Stark and neighboring counties.
by Climate Science, April 8, 2018
As the U.K. celebrates its final year as part of the European Union, it is standing on the brink of a major boost to its economy and prosperity as it awaits the first economic benefit from its rich oil and gas shales (…)
by P. Homewood, April 8, 2018 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
Bit by bit, some reality appears to be intruding into the make believe world of the Climate Change Act:
No credible scenario’ exists for hitting the UK’s 2050 decarbonisation targets without continued reliance on gas, the National Grid has warned.
In a new report, entitled The Future of Gas: How gas can support a low carbon future’, the grid says that it is not feasible to switch over to electric heating on the scale required to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to 80 per cent of 1990 levels by the middle of this century.
by Catherine Philp, April 5, 2018 in TheTimes
Sheikh Mohammed bin Khalifa al-Khalifa said it was not yet known how much of the oil could be extracted. The scale of the find, however, is about to make it a big player in the global market, significantly boosting its economy and raising its profile in the region, where it plays a smaller fiddle to its giant neighbour, Saudi Arabia.
See also here
by P. Homewood, April 3, 2018 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
A joint report by Greenpeace, the Sierra Club and CoalSwarm indicates that Southeast Asia will be the new epicentre of coal production. Asia accounts for 85 per cent of new coal power development in the world’s top 20 coal producing countries, with China as the leader of the pack. However, while tighter restrictions on domestic coal plants have been imposed by the central government to curb pollution, Beijing has pushed the development of high-efficiency, low-emission coal plants across Southeast Asia as part of the “Belt and Road Initiative”.
As China is expanding its influence, Beijing’s foremost strategic competitor in Asia, Japan, is being forced to step up efforts to combat its shrinking influence in the region. The booming energy sector of Southeast Asia, especially coal, is proving to be the new front line in the geopolitical rivalry between Asia’s two industrial giants.
by P. Homewood, March 29, 2018 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
Just as a follow up to my earlier post on German GHG emissions, I have looked at the comparative energy consumption figures for 2009 and 2016 (…)
by Kelly Gilblom, March 26, 2018 in BloombergMarkets
The world’s largest oil companies have survived a life-changing crisis, and are now poised to reap the rewards, Goldman Sachs Group Inc. said.
Big Oil is in a sweet spot with rising oil prices and low operating costs, leaving them with the biggest cash-flow growth in two decades and boosting earnings, Goldman said in a report Monday. That will increase their attraction for investors after years of elevated spending followed by crude’s slump sent their weighting in global equity indexes to a 50-year low, according to the bank (…)
by M. Bastach, March 19, 2018 in TheDailyCaller
U.S. exported more natural gas in 2017 than it imported for the first time in 60 years, according to the Energy Department.
Natural gas production has boomed in recent years, particularly in Pennsylvania and other parts of Appalachia, thanks to hydraulic fracturing or fracking and horizontal drilling. The boom has offset Canadian imports and allowed U.S. companies to ship more fuel abroad.
by P. Homewood, March 18, 2018 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
GWPF brings us the story, originally published by the Daily Maverick, of how South African academics are pushing the frontiers of clean coal (…)
by L’essentiel, 18 mars 2018
Grâce à une production de pétrole en plein boom, les États-Unis exportent désormais sans complexe leur or noir dans le monde, entraînant une refonte des infrastructures sur leur territoire et rebattant les cartes sur le marché mondial. En pompant actuellement plus de 10 millions de barils par jour, le pays est devenu le deuxième producteur de brut au monde, derrière la Russie et devant l’Arabie saoudite. Un essor lié aux nouvelles techniques permettant d’extraire à moindre coût du pétrole de schiste
by PennEnergy Editorial Staff, February 2, 2018
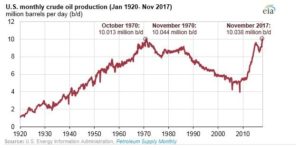
U.S. crude oil production reached 10.038 million barrels per day (b/d) in November 2017, according to EIA’s latest Petroleum Supply Monthly. November’s production is the first time since 1970 that monthly U.S. production levels surpassed 10 million b/d and the second-highest U.S. monthly oil production value ever, just below the November 1970 production value of 10.044 million b/d.
Within the Lower 48 states, November 2017 production reached a record high in Texas at 3.89 million b/d, followed by North Dakota at 1.18 million b/d. Production in the Federal Gulf of Mexico reached 1.67 million b/d, up 14% from the October 2017 level as the region recovered from Hurricane Nate.
by BP Global, March 2018
The Energy Outlook explores the forces shaping the global energy transition out to 2040 and the key uncertainties surrounding that transition. It shows how rising prosperity drives an increase in global energy demand and how that demand will be met over the coming decades through a diverse range of supplies including oil, gas, coal and renewables.
Looking forward to 2040
Extending the Energy Outlook by five years to 2040, compared with previous editions, highlights several key trends.
For example, in the ET scenario, there are nearly 190 million electric cars by 2035, higher than the base case in last year’s Outlook of 100 million. The stock of electric cars is projected to increase by a further 130 million in the subsequent five years, reaching around 320 million by 2040.
Another trend that comes into sharper focus by moving out to 2040 is the shift from China to India as the primary driver of global energy demand. The progressively smaller increments in China’s energy demand – as its economic growth slows and energy intensity declines – contrasts with the continuing growth in India, such that between 2035 and 2040, India’s demand growth is more than 2.5 times that of China, representing more than a third of the global increase.
Africa’s contribution to global energy consumption also becomes more material towards the end of the Outlook, with Africa accounting for around 20% of the global increase during 2035-2040; greater than that of China.
by D. Middleton, March 8, 2018 in WUWT
Not quite a year ago (April 18, 2017) I authored a post on the completion of the Petra Nova carbon capture project at the W. A. Parrish coal-fired power plant in Fort Bend County, Texas. Petra Nova was billed as “the largest post-combustion carbon capture project in the world.” In addition to capturing CO2 from a very large coal-fired power plant, Petra Nova was also designed to serve a useful purpose: Deliver CO2 for enhanced oil recovery to West Ranch Oil Field in Jackson County, Texas. The ultimate goal is to boost production in the field from around 500 barrels of oil per day (BOPD) to 15,000 BOPD and recover about 60 million barrels that would otherwise have been left in the ground.
EIA had an update on the carbon capture aspect back in October…
by J. Worland, March 6, 2018 in Time
The widespread adoption of fracking in the U.S. opened billions of barrels of oil and trillions of cubic feet of natural gas to production and transformed the global energy sector in a matter of a few years. Now, a leading global energy agency says U.S. natural gas is about to do it again.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) said in a new forecast this week that growth in U.S. oil production will cover 80% of new global demand for oil in the next three years. U.S. oil production is expected to increase nearly 30% to 17 million barrels a day by 2023 with much of that growth coming from oil produced through fracking in West Texas.
by W. Mahdi and B. Stanley, March 7, 2018 in Bloomberg
Saudi Aramco, the world’s largest oil exporter, is set to join the shale revolution with plans to start producing unconventional natural gas this month and exploit a deposit that could rival the Eagle Ford formation in Texas.
Saudi Arabia’s gas resources from shale and other alternative supplies are “huge,” Khalid Al Abdulqader, general manager of unconventional resources at Aramco, said Wednesday in Manama, Bahrain. Production at the kingdom’s North Arabia basin will start by the end of March and reach its target by the end of this year, he said, without giving details.
by R. Heinberg, March 6, 2018 in Resilience.org
Well, I’m amazed and impressed. Tight oil production has pushed total United States petroleum output to more than 10 million barrels a day, a rate last seen almost a half-century ago. It’s a new U.S. record. Fifteen years ago I was traveling the world with a Powerpoint presentation featuring a graph of U.S. oil production history. That graph showed a clear peak in 1970 and a long bumpy decline thereafter. (…)
by Francis Menton, February 25, 2018 in ManhattanContrarian
Every day you read about the crisis of climate change and fossil fuel usage and CO2 emissions, and commitments from politicians around the world to “act” to “save the planet.” Surely then, CO2 emissions are in steep decline and headed for zero.
The truth is of course the opposite. In the developed world, rapidly increasing use of “renewables” like intermittent wind and solar energy only serves to drive electricity prices through the roof, while having only the most marginal effect on reducing emissions.
by J. Hodges and K. Gilblom, March 2, 2018 in BusinessDay
London — Britain’s natural gas fracking industry is using a cold snap that’s gripped large swathes of Europe this week and laid bare weaknesses in the UK’s energy supply to make its pitch.
Britain’s natural gas market has been stretched to its limits as the coldest spell since 2010 tests the nation’s energy and transport network. UK pipeline manager National Grid Plc even urged industry to curb its gas usage while the cold weather persisted. (…)