by Dr. J. Lehr & J. Taylor, January 6, 2020 in CFACT
A recently published paper, titled “Evaluating the Performance of Past Climate Model Projections,” mistakenly claims climate models have been remarkably accurate predicting future temperatures. The paper is receiving substantial media attention, but we urge caution before blindly accepting the paper’s assertions.
As an initial matter, the authors of the paper are climate modelers. Climate modelers have a vested self-interest in convincing people that climate modeling is accurate and worthy of continued government funding. The fact that the authors are climate modelers does not by itself invalidate the paper’s conclusions, but it should signal a need for careful scrutiny of the authors’ claims.
Co-author Gavin Schmidt has been one of the most prominent and outspoken persons asserting humans are creating a climate crisis and that immediate government action is needed to combat it. Again, Schmidt’s climate activism does not by itself invalidate the paper’s conclusions, but it should signal a need for careful scrutiny of the authors’ claims.
The paper examines predictions made by 17 climate models dating back to 1970. The paper asserts 14 of the 17 were remarkably accurate, with only three having predicted too much warming.
One of the paper’s key assertions is that global emissions have risen more slowly than commonly forecast, which the authors claim explains why temperatures are running colder than the models predicted. The authors compensate for this by adjusting the predicted model temperatures downward to reflect fewer-than-expected emissions. Yet fewer-than-expected greenhouse gas emissions undercut the climate crisis narrative.
The U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has already reduced its initial projection of 0.3 degrees Celsius of warming per decade to merely 0.2 degrees Celsius per decade. Keeping in mind that skeptics have typically predicted approximately 0.1 degree Celsius of warming per decade, the United Nations has conceded skeptics have been at least as close to the truth with their projections as the United Nations. Moreover, global temperatures are likely only rising at a pace of 0.13 degrees Celsius per decade, which is even closer to skeptic predictions.
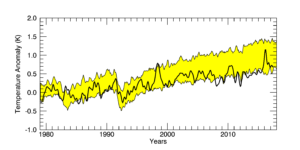
Even after the authors adjusted the model predictions to reflect fewer-than-expected greenhouse gas emissions, there remains at least one very important problem, which immediately jumped out at us when carefully examining the paper’s findings: The paper’s assertion of remarkable model accuracy rests on a substantial temperature spike from 2015 through 2017. A strong, temporary El Niño caused the short-term spike in global temperatures from 2015 to 2017. The plotted temperature data in the paper, however, show that temperatures prior to the El Niño spike ran consistently colder than the models’ adjusted predicted temperatures. When the El Niño recedes, as they always do, temperatures will almost certainly resume running colder than the models predicted, even after adjusting for fewer-than-expected greenhouse gas emissions.
Another problem with the paper is that it utilizes controversial and dubiously adjusted temperature datasets rather than more reliable ones. The paper relies on temperature datasets that are not replicated in any real-world temperature measurements. Surface temperature measurements and measurements taken by highly precise satellite instruments show significantly less warming than the authors claim. The authors rely on temperature datasets that utilize controversial adjustments to claim more recent warming than what has actually been measured, which further undercuts their claim of remarkable model accuracy.
Contrary to what has been written in many breathless media reports, the most important takeaways from the paper are that greenhouse gas emissions are rising at a more modest pace than predicted, the modest pace of global temperature rise reflects the modest pace of rising emissions, and climate models have consistently predicted too much warming—even after accounting for fewer-than-expected greenhouse gas emissions. A temporary spike in global temperatures reflecting the recent El Niño does not save the models from their consistent inaccuracy.
