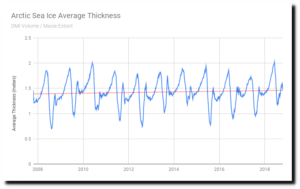
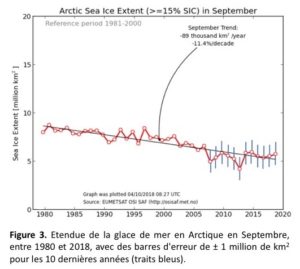
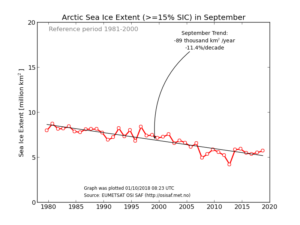
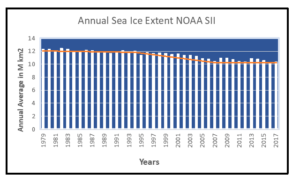
by GWPF, December 7, 2018
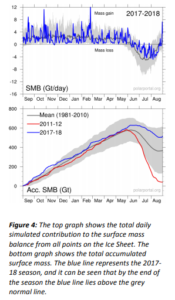
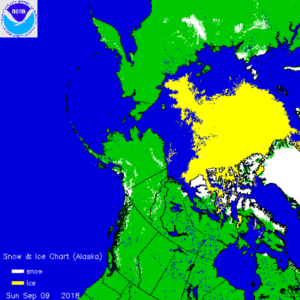
The Danish Meteorological Institute (DMI) also performs daily simulations of how much ice or water the Ice Sheet loses or accumulates. Based on these simulations, an overall assessment of how the surface mass balance develops across the entire Ice Sheet is obtained (Fig. 4).
At the end of the 2018 season (31 August 2018), the net surface mass balance was 517 Gt, which means that 517 Gt more snow fell than the quantity of snow and ice that melted and ran out into the sea. This number only contains the balance at the surface, and thus not the total balance, which also includes melting of glaciers and calving of icebergs.
…
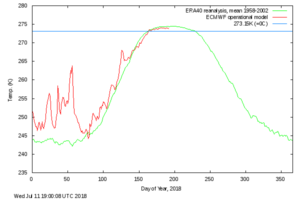
Although the total SMB (Surface Mass Budget) for the 2016-2017 and 2017-2018 seasons are similar, development during the two seasons has been very different. Last year, the season began by gaining a lot of mass during the winter, whilst the development in SMB from the summer onwards reflected the long-term average. During the 2017-2018 season, SMB remained in line with the average from 1981-2010 until the summer, after which the development in SMB was higher than average.