by Cap Allon, Apr 30, 2021 in Electroverse
GALACTIC Cosmic Rays are a mixture of high-energy photons and sub-atomic particles accelerated toward Earth by supernova explosions and other violent events in the cosmos, while SOLAR Cosmic Rays are effectively the same, only their source is the Sun.
Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus have been launching cosmic ray balloons almost weekly since March 2015–before the pandemic threw a spanner in. The team’s published results reveal that atmospheric radiation reached record highs just as solar activity hit a new space age low — the correlation is clear for all to see, with additional proxy data revealing it has been the case for time-immemorial.
During solar minimums –the low point of the 11 year solar cycle– the Sun’s magnetic field weakens and the outward pressure of the solar wind decreases. This allows more cosmic rays (CRs) to penetrate the inner solar system, including our planet’s atmosphere:
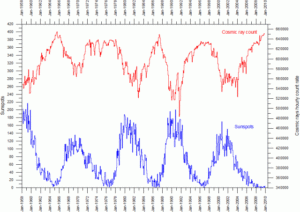
Cosmic Rays correlating with Sunspots.
…
by P. Gosselin, May 5, 2021 in NoTricksZone
To find out what the global snowfall trend has been, the hotshot data analyst diligently downloaded all available monthly NASA images from 1980 to 2020 (inclusive), such as the one shown below, and then converted the pixel colors back to data using the provided scale.
…
…
Here over the past 40 years snowfall has indeed grown from 0.6257 to 0.7057 decigrams/m2/s, or +12.77%. This trend, like many, is not global.
It just goes to show that when it comes to the chaotic system of climate, things are never simple and researchers get surprised almost daily.
You can generate your own charts using data archived here.
by Popular Technology.net Aug 21, 2016
The following lectures from the Prager University Foundation cover climate change, energy and the environment. The Prager University Foundation, a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization has created an online resource of concise five minute lectures on environmental science topics presented by scientific experts and professionals. These offer fresh perspectives supported by fact based reasoning on contentious issues to anyone with an open mind.
“A world of new perspectives, five minutes at a time.” – Prager University Foundation
…
See the videos
by Cap Allon, May, 3, 2021, in Electroverse
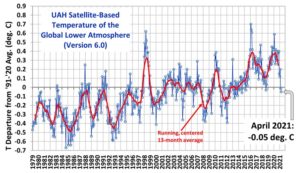
The Version 6.0 global average lower tropospheric temperature (LT) anomaly for April, 2021 has come in at -0.05 deg. C, sinking further below the 30-year baseline down from the March, 2021 value of -0.01 deg. C, and down substantially (approx. 0.65C deg. C) from where we were around a year ago…
…in other words, it is get harder and harder for the politicized ‘catastrophic global heating’ narrative to be maintained. But as Gustave Le Bo writes: “The masses have never thirsted after truth. They turn aside from evidence that is not to their taste, preferring to deify error, if error seduces them. Whoever can supply them with illusions is easily their master; whoever attempts to destroy their illusions is always their victim.”
A continuation of this downward plunge is probable over the coming months (with the odd bump along the way–climate is cyclic after all) as low solar activity and La Nina conditions continues to influence our climate.
According to the 15x NASA/NOAA AMSU satellites that measure every square inch of the lower troposphere (where us humans reside), planet Earth was actually warmer back in 1980:
…
Solar Cycle 25 may have finally started stirring (see link below), but sunspots (a great barometer for solar activity) look set to closely track the forecasts: i.e., the cycle is due to be another weak one, similar in vein to the cycle just gone (24), which will continue the global cooling trend that is now firmly established.
…
by M. Sigl et al., Jan 8, 2018 in TheCryosphere
…
Starting around AD 1860, many glaciers in the European Alps began to retreat from their maximum mid-19th century terminus positions, thereby visualizing the end of the Little Ice Age in Europe. Radiative forcing by increasing deposition of industrial black carbon to snow has been suggested as the main driver of the abrupt glacier retreats in the Alps. The basis for this hypothesis was model simulations using elemental carbon concentrations at low temporal resolution from two ice cores in the Alps.
Here we present sub-annually resolved concentration records of refractory black carbon (rBC; using soot photometry) as well as distinctive tracers for mineral dust, biomass burning and industrial pollution from the Colle Gnifetti ice core in the Alps from AD 1741 to 2015. These records allow precise assessment of a potential relation between the timing of observed acceleration of glacier melt in the mid-19th century with an increase of rBC deposition on the glacier caused by the industrialization of Western Europe. Our study reveals that in AD 1875, the time when rBC ice-core concentrations started to significantly increase, the majority of Alpine glaciers had already experienced more than 80 % of their total 19th century length reduction, casting doubt on a leading role for soot in terminating of the Little Ice Age. Attribution of glacial retreat requires expansion of the spatial network and sampling density of high alpine ice cores to balance potential biasing effects arising from transport, deposition, and snow conservation in individual ice-core records.
…
by A. Lawrence_Mathers, Apr 1, 2021 PhysicsToday
In August 1861 the London-based newspaper The Times published the world’s first “daily weather forecast.” The term itself was created by the enterprising meteorologist Robert FitzRoy, who wanted to distance his work from astrological “prognostications.” That story has led to a widespread assumption that weather forecasting is an entirely modern phenomenon and that in earlier periods only quackery or folklore-based weather signs were available.
…
…
La géologie, une science plus que passionnante … et diverse


