by D. Neufeld, Aug 22, 2025 in VisualCapitalist
The Global Energy Mix in 2024
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Key Takeaways
- Global energy demand increased 2% to reach an all-time high of 592 exajoules (EJ) in 2024.
- Non-fossil fuels grew 7% year-over-year, bringing their share of the global energy mix to 13.5%.
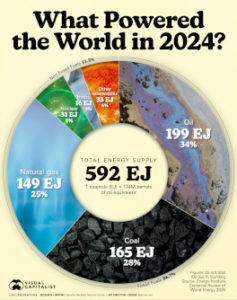
Global energy use rose to 592 EJ in 2024, marking a new record in demand.
While cleaner technologies continue to expand, traditional energy sources still form the backbone of the global energy system. At the same time, the Asia Pacific region drove 68% of demand growth, reflecting the region’s rapid economic momentum and industrialization.
This chart shows the global energy mix in 2024, based on data from the Energy Institute.
Fossil Fuels Underpin the Global Energy Mix
Last year, oil, coal, and natural gas together supplied 86.7% of global energy needs.
Oil remained the dominant energy source, accounting for 199 EJ, or 33.6% of global supply. In 2024, average oil prices declined by 3%, though they were still 27% higher than in 2019. The U.S. held its position as the world’s largest producer, contributing roughly one-fifth of total output.
Coal followed at 27.9%, supported by increased consumption in emerging economies. Natural gas, though cleaner than coal, supplied 25.2%, rounding out the fossil fuel trio.
| Energy Source | 2024 Total Energy Supply (EJ) | Share |
|---|---|---|
| Oil | 199 | 33.6% |
| Coal | 165 | 27.9% |
| Natural gas | 149 | 25.2% |
| Nuclear energy | 31 | 5.2% |
| Hydroelectricity | 16 | 2.7% |
| Other renewables | 33 | 5.6% |
| Total | 592 |
It’s also worth noting that low-carbon energy sources are growing at a meaningful pace.
In 2024, their combined share rose to 13.5%, supported by a 7% annual increase. Wind and solar stood out in particular, growing by 16% to remain the fastest-rising energy sources worldwide.
Moreover, nuclear energy accounted for 5.2% of supply, with France and Japan responsible for nearly two-thirds of its growth as long-idled plants were brought back online.
…




































































