| 1. The “Greenhouse Effect” is a natural and valuable phenomenon, without which, the planet would be uninhabitable.2. Modest Global Warming, at least up until 1998 when a cooling trend began, has been real.
3. CO2 is not a significant greenhouse gas; 95% of the contribution is due to Water Vapor.
4. Man’s contribution to Greenhouse Gasses is relatively insignificant. We didn’t cause the recent Global Warming and we cannot stop it.
5. Solar Activity appears to be the principal driver for Climate Change, accompanied by complex ocean currents which distribute the heat and control local weather systems.
6. CO2 is a useful trace gas in the atmosphere, and the planet would actually benefit by having more, not less of it, because it is not a driver for Global Warming and would enrich our vegetation, yielding better crops to feed the expanding population.
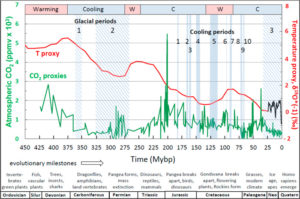
7. CO2 is not causing global warming, in fact, CO2 is lagging temperature change in all reliable datasets. The cart is not pulling the donkey, and the future cannot influence the past.
8. Nothing happening in the climate today is particularly unusual, and in fact has happened many times in the past and will likely happen again in the future.
9. The UN IPCC has corrupted the “reporting process” so badly, it makes the oil-for-food scandal look like someone stole some kid’s lunch money. They do not follow the Scientific Method, and modify the science as needed to fit their predetermined conclusions. In empirical science, one does NOT write the conclusion first, then solicit “opinion” on the report, ignoring any opinion which does not fit their predetermined conclusion while falsifying data to support unrealistic models.
10. Polar Bear populations are not endangered, in fact current populations are healthy and at almost historic highs. The push to list them as endangered is an effort to gain political control of their habitat… particularly the North Slope oil fields.
11. There is no demonstrated causal relationship between hurricanes and/or tornadoes and global warming. This is sheer conjecture totally unsupported by any material science.
12. Observed glacial retreats in certain select areas have been going on for hundreds of years, and show no serious correlation to short-term swings in global temperatures.
13. Greenland is shown to be an island completely surrounded by water, not ice, in maps dating to the 14th century. There is active geothermal activity in the currently “melting” sections of Greenland.
14. The Antarctic Ice cover is currently the largest ever observed by satellite, and periodic ice shelf breakups are normal and correlate well with localized tectonic and geothermal activity along the Antarctic Peninsula.
15. The Global Warming Panic was triggered by an artifact of poor mathematics which has been thoroughly disproved. The panic is being deliberately nurtured by those who stand to gain both financially and politically from perpetuation of the hoax.
16. Scientists who “deny” the hoax are often threatened with loss of funding or even their jobs.
17. The correlation between solar activity and climate is now so strong that solar physicists are now seriously discussing the much greater danger of pending global cooling.
18. Biofuel hysteria is already having a disastrous effect on world food supplies and prices, and current technologies for biofuel production consume more energy than the fuels produce.
19. Global Warming Hysteria is potentially linked to a stress-induced mental disorder.
20. In short, there is no “climate crisis” of any kind at work on our planet. |