by Anthony Watts, April 4, 2018 in WUWT
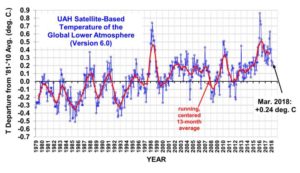
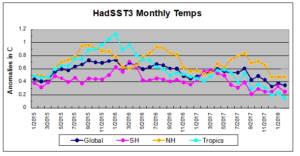
March temperatures (preliminary)
Global composite temp.: +0.24 C (about 0.43 degrees Fahrenheit) above 30-year average for March.
Northern Hemisphere: +0.39 C (about 0.70 degrees Fahrenheit) above 30-year average for March.
Southern Hemisphere: +0.10 C (about 0.18 degrees Fahrenheit) above 30-year average for March.
Tropics: +0.06 C (about 0.11 degrees Fahrenheit) above 30-year average for March.
February temperatures (revised):
Global Composite: +0.20 C above 30-year average
Northern Hemisphere: +0.24 C above 30-year average
Southern Hemisphere: +0.15 C above 30-year average
Tropics: +0.03 C above 30-year average
(All temperature anomalies are based on a 30-year average (1981-2010) for the month reported.)