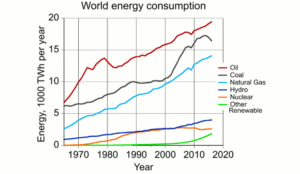
by A. Watts, November 21, 2019 in WUWT
Research & Commentary by Tim Benson
A new report prepared by Kleinhenz & Associates for the Ohio Oil and Gas Energy Education Program shows increased oil and natural gas production from hydraulic fracturing (“fracking”) has saved American consumers $1.1 trillion in the decade from 2008 to 2018. This breaks down to more than $900 in annual savings to each American family, or $9,000 in cumulative savings. Continuer la lecture de New Report Says Fracking Saved Americans $1.1 Trillion Over Past Decade

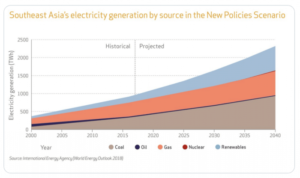
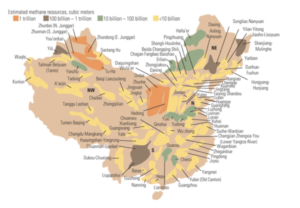
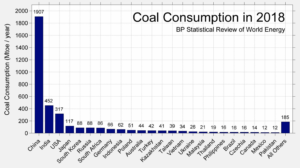
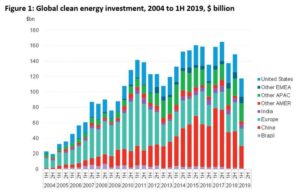
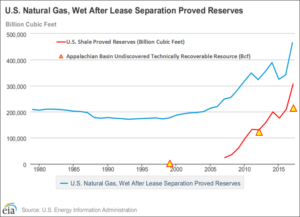 Figure 2. “The effects American ingenuity and new technology can have.”…
Figure 2. “The effects American ingenuity and new technology can have.”…