by Climate at a Glance, June 1, 2020 in ClimateChangeDispatch
The COVID-19, aka Coronavirus pandemic, is causing a worldwide shutdown in economic activity as businesses close, airlines cancel flights, energy production is reduced, and people shelter in their homes and drive less.
Climate activists expected this economic downtown to translate to less energy usage, and therefore less CO2 emissions globally.
While that has indeed happened, with China seeing a 40% emissions drop, and an expected 11% reduction in energy-related CO2 emissions in the U.S. this year, it didn’t translate into the proof they were seeking.
What scientists are looking for is any evidence of a decline in global atmospheric CO2 concentrations that would be strong enough to attribute to the economic downturn.
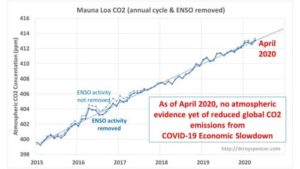
University of Alabama climate scientist Dr. Roy Spencer used a simple method1 for removing the large seasonal CO2 cycle2, due to plant photosynthesis increases/decreases with seasons, from the Mauna Loa CO2 data, and well as the average effects from El Nino and La Nina events, which change the rate of ocean outgassing of CO2.
The result: no obvious downtown in global CO2 levels has been observed3,4.
As can be seen in Figure 1, the latest CO2 data show no downtrend, but instead just a ripple, that is not unlike other ripples in the graph when there was no crisis and resulting economic downturn.
Figure 1: Using a simple method1 for removing the large seasonal cycle from the Mauna Loa CO2 data, and well as the average effects from El Nino and La Nina events, no obvious downtown in global CO2 levels has been observed4. Analysis by Dr. Roy Spencer.