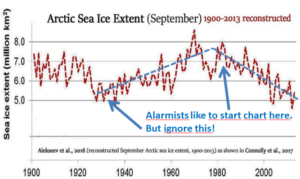
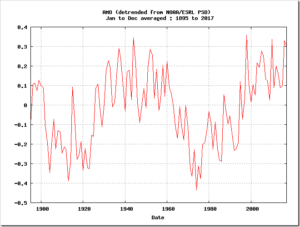
by Anthony Watts, August 30, 2018 in WUWT
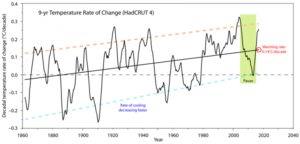
Earth’s surface has undergone unprecedented warming over the last century, and especially in this century.
Every single year since 1977 has been warmer than the 20th century average, with 16 of the 17 warmest years on record occurring since 2001, and 2016 being the warmest year on recorded history. A study from 2016 found that without the emissions from burning coal and oil, there is very little likelihood that 13 out of the 15 warmest years on record would all have happened.
Source: https://www.ucsusa.org/global-warming/science-and-impacts/science/human-contribution-to-gw-faq.html
First a definition of the word “unprecedented”:
…
Note that “in this century” isn’t part of the definition. it says “never done or known before”
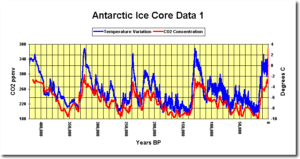
So in that spirit, here’s some other “unprecedented” warming in Earth’s history, via the Vostok Ice Core dataset:
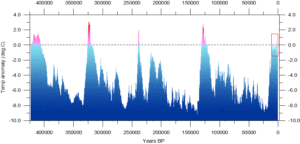
…