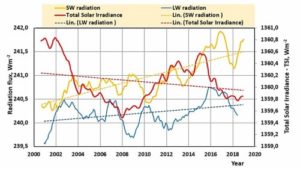
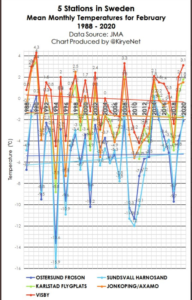
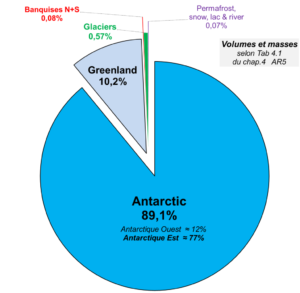
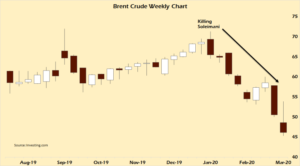
by Andy May, March 21, 2020 in WUWT
…
…
C3S20 asks, how much human-caused warming will occur if we do nothing, that is, continue “business-as-usual?” It’s unfortunate, but the IPCC, for all their work, do not adequately answer that question, their projections are all based on abstract “scenarios.” C3S20 break this overall question into five parts:
- What would greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) be, if we did nothing and continued normally?
- For each GHG, how do emissions relate to the change in atmospheric concentration?
- What would the global temperature be if GHG concentrations were at “preindustrial” levels?
- How sensitive are global temperatures to GHG concentrations?
- How much warming should we expect if we do nothing?
C3S20 tell us the Paris Agreement conclusion that we need to limit global warming to 2°C above preindustrial levels suffers from several unknowns.
-
The preindustrial period is not formally defined. The preindustrial temperature and greenhouse gas level are not specified. In fact, several time periods, temperatures and GHG levels are used as “preindustrial” in the latest IPCC AR5 report.
-
The assumptions that warming is bad and increasing levels of CO2 are bad, are not supported with any data. Numerous studies have concluded that some warming is good for humankind and additional CO2 is good for plants.
-
The penultimate draft of AR5 identified the period 1850 to 1900 as the preindustrial baseline for CO2 and temperature. This was the end of the Little Ice Age, the coldest periodin the last several thousand years. Why use that period as a baseline (Luning and Vahrenholt 2017)? This is not explained, and the final draft of the report removed the reference to the 1850 to 1900 baseline.
-
If the UNFCC and the Paris Agreement assume “climate change” and “Human-caused Climate Change” are synonymous, how do they explain that climate has change much quicker and much more dramatically many times in the past 13,000 years before human civilization began and well before industrialization?
…