by Shane Hoover, April 4, 2018 in Inde.Online.com
Utica Midstream conference gives update on Utica Shale production and development.
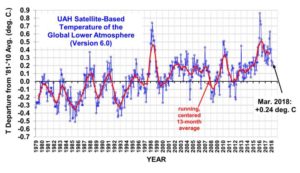
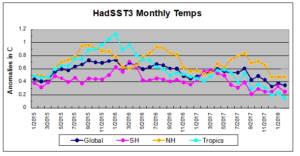
NORTH CANTON Ohio has produced more natural gas than it uses since early 2015. Driven by prolific Utica Shale wells, the state produced a record 1.7 trillion cubic feet of natural gas last year.
Much of the regional economic development around that production has been in the form of pipelines and processing facilities.
Two interstate natural gas pipelines — Energy Transfer’s Rover project and the NEXUS Gas Transmission pipeline — cross Stark and neighboring counties.