by J. Steele, Oct 1, 2023 in WUWT
Why climate models not yet worth their salt!
As all hurricane researchers lament, model predictions of when and where hurricanes will intensify, have not improved much in the past 20 years. As recently as the early 2010s, weather model forecasts failed to predict 88 percent of rapidly intensifying tropical storms. Nonetheless National Public Radio (NPR) has ranted that hurricanes are “intensifying more quickly, turning from less-serious storms to very strong ones in hours or days. Superheated ocean waters hold a lot of extra energy, and a growing storm can draw from that enormous pool.” But such “superheated water” is not widespread as rising CO2 narratives suggest, but found only in very limited regions and usually associated with “barrier layers”.
Hurricanes intensify as they draw “superheated” subsurface waters of 65.5°F or higher. However, when a hurricane’s suction pulls up cooler subsurface waters, the hurricane weakens. This negative feedback naturally limits the intensity of all hurricanes. In the upper panel of the attached graphic, Arnand (2023) illustrates where thin barrier layer exists, hurricane intensity hovers around Category 1. In contrast, where thick barrier layers form, cooler deep waters are prevented from reaching the surface, and instead allow superheated sub-surface waters to cause rapid intensification.
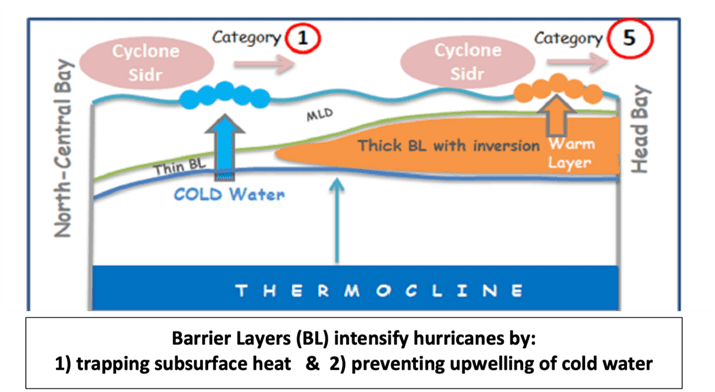
Denser fluids don’t naturally rise above less dense fluids! Barrier layer formation happens wherever freshwater overlays dense salty waters. Although solar heating would normally make subsurface waters less dense and rise to the surface, layers with higher saltiness makes the water more dense which inhibits warm convection. That traps and intensifies the subsurface heat, enabling hurricanes to intensify to Category 5.
…
