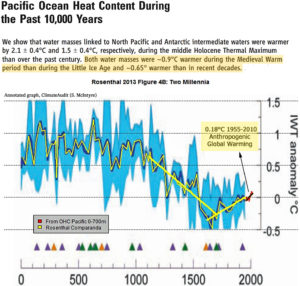
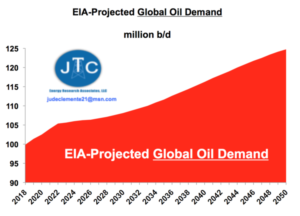
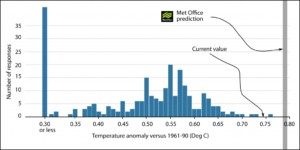
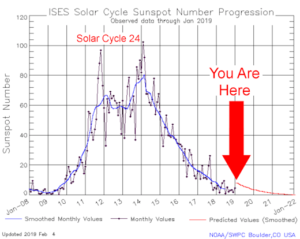
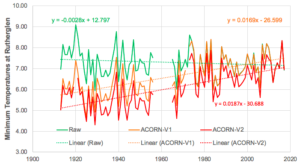
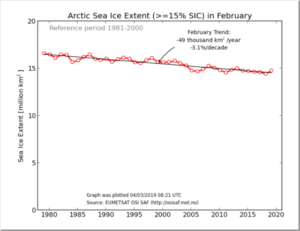
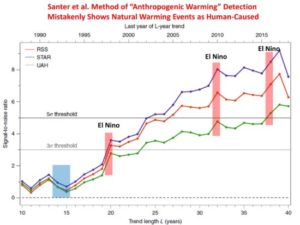
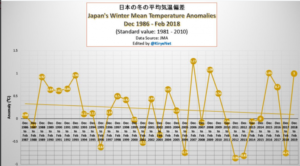
by Charles the moderator, March 11, 2019 in WUWT
New York (CNN Business)Move over, Saudi Arabia. America is about to steal the kingdom’s energy exporting crown.
The United States will surpass Saudi Arabia later this year in exports of oil, natural gas liquids and petroleum products, like gasoline, according to energy research firm Rystad Energy.
That milestone, driven by the transformative shale boom, would make the United States the world’s leading exporter of oil and liquids. That has never happened since Saudi Arabia began selling oil overseas in the 1950s, Rystad said in a report Thursday.
“It’s nothing short of remarkable,” said Ryan Fitzmaurice, energy strategist at Rabobank. “Ten years ago, no one thought it could happen.”
The expected breakthrough reflects how technology has reshaped the global energy landscape. Drilling innovations have opened up huge swaths of oil and natural gas resources that had been trapped in shale oilfields in Texas, North Dakota and elsewhere.
Led by shale, US oil production has more than doubled over the past decade to all-time highs. The United States now pumps more oil than any other country, including Russia and Saudi Arabia.
“The shale boom has driven incredible increases in production,” said Fitzmaurice. “US production is off the charts.”
…