by P. Homewood, March 28, 2021 in IowaClimSciEducation

The Upper & Lower Grindelwald Glaciers in 1774 by Caspar Wolf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caspar_Wolf
HH Lamb’s Climate, History and The Modern World tells us much about the history of Alpine glaciers. For instance, how they advanced rapidly between 800 and 400 BC. They then retreated before advancing again between AD 600 and AD 850, when they may have even reached Little Ice Age maximum extents.
We are probably all familiar with the terrifying glacier advances, which began in the 17thC, following centuries of a much warmer climate. These were catastrophic for anybody living nearby, as farming land was wiped out, and even the land that escaped being overrun was far too cold to farm. As a result, famine was rife in Switzerland and elsewhere, even in cities which relied on the countryside for food.
People living in those days would have been dumfounded to hear that there are some now who are worried that glaciers are getting smaller.
A paper by Zumbuhl et al, published in 2006, offers a detailed history of the Lower Grindelwald glacier, as well as the Mer de Glace in the Mont Blanc region:
…
by P. Gosselin, March 28 in NoTricksZone
Antarctic sea ice grows 2 million square kilometers in 4 years…
It’s hard to back up the statement: Global warming is global. Some places have seen warming over the past 40 years (e.g. Arctic), but other places have not.
Antarctica definitely has not been playing along with the man-made global warming hoax. (Yes, man has caused some of the warming, but not all – and it certainly isn’t catastrophic).
Antarctic sea ice surges
Though Antarctic sea ice fell to a “record minimum” in 2017 – after having reached a “record high” in 2015 – the latest data from the National Snow and Ice Data Centershow sea ice at the South Pole has bounced back robustly since, surging some 500,000 sq km above the mean.
On March 26, 2017, Antarctic sea ice measured 3.055 million sq km. Four years later, sea ice reached 5.103 million sq km. That’s a difference of more than 2 million sq. km., which is an area the size of Saudi Arabia!
No way to ignore natural factors
So why would sea ice grow so quickly? If the ice had disappeared, many would blame it on greenhouse gases – absurd of course. And it would be just as absurd to blame the recent gain on global cooling. Obviously there is a complex array of natural factors at work – factors that climate alarmists consistently have ignored over the past decades.
Here’s the March 26, 2021 satellite photo of Antarctica:
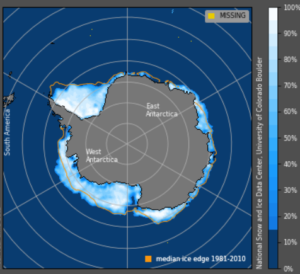
Source: NSIDC
…
La géologie, une science plus que passionnante … et diverse


