by C. Rotter, Aug 24, 2024 in WUWT
Maguire’s article, which is as much a lament as it is a piece of journalism, paints Florida as the villain in a story where the rest of the country is the hero, gallantly marching toward a green utopia. But here’s the kicker: Florida’s doing just fine, and the people who live there know it. Let’s break down the absurdity of the climate scolds and see why Florida’s energy strategy is not only sensible but downright smart.
Fossil Fuels: The Workhorse of Florida’s Energy Grid
According to Maguire, Florida’s reliance on fossil fuels—gasp—has actually increased in 2024, a move that he seems to think is tantamount to environmental heresy. “Florida reverses energy transition by cranking fossil fuel use,” his headline wails, as if the state had suddenly decided to reverse gravity. But let’s get real: fossil fuels, particularly natural gas, are the backbone of Florida’s energy grid for a very simple reason—they work. When the summer sun is beating down, and everyone’s cranking up the AC, no one wants to hear that their power has been cut because the wind isn’t blowing or a cloud passed over a solar farm.
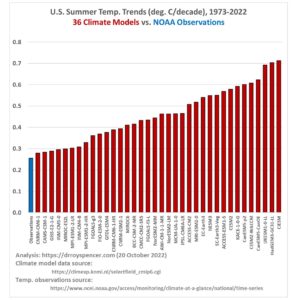
Maguire points out that over 80% of Florida’s electricity has come from fossil fuels since the beginning of June, the highest share in over three years. He compares this to the national average of 62.4% and Texas’s 62%, as if this somehow proves Florida is an outlier in the worst way. But let’s be honest: these are numbers that should make Floridians proud. While the rest of the country toys with unreliable renewables, Florida is ensuring that its citizens have a reliable, affordable energy supply.
The Reality of Renewable Energy
Renewables sound great on paper, don’t they? Free energy from the sun and wind—what’s not to love? But here’s where the rubber meets the road: renewables aren’t ready for prime time, especially not in a state like Florida, where reliability isn’t just a luxury, it’s a necessity. Imagine the chaos if millions of Floridians were left in the sweltering heat because the sun decided to take a day off. Florida’s summer is no joke, and neither is the demand for electricity. The state’s grid needs to be as robust as a linebacker, not as fragile as a flower.
And it’s not like Florida has completely ignored renewable energy. Florida Power & Light (FPL), the largest utility in the state, is leading a solar charge, aiming to install 30 million solar panels by 2030. But here’s the kicker—Florida’s leaders know that solar is a supplement, not a substitute. That’s why they haven’t thrown the baby out with the bathwater and abandoned fossil fuels.
…