by Willis Eschenbach, January 18, 2020 in WUWT
…
Folks are interested in why the temperature of the planet changes over time. That’s at the center of modern climate science. My theory, on the other hand, arose from my being interested in a totally different question about climate—why is the temperature so stable? For example, over the 20th Century, the temperature only varied by ± 0.3°C. In the giant heat engine that is the climate, which is constantly using solar energy to circulate the oceans and the atmosphere, this is a variation of 0.1% … as someone who has dealt with a variety of heat engines, I can tell you that this is amazing stability. The system is ruled by nothing more solid than waves, wind, and water. So my question wasn’t why the climate changes as it does.
My question was, why is the climate so stable?
And my answer is, there are a host of what are called “emergent phenomena” that arise when local temperatures go above some local threshold. They include the timing and strength of the daily emergence of the cumulus cloud field in the tropics; the development of thunderstorms; the emergence of dust devils when temperatures get hot; the action of the El Nino/La Nina pump moving warm water to the poles; and various “oscillations” like the Pacific Decadal Oscillation.
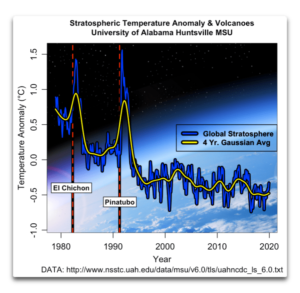
These emergent phenomena arise out of nowhere, last for some length of time, and then disappear completely. And acting together, they all work to prevent both the overcooling and the overheating of the planet. And as mentioned above, I say that these phenomena acted to reduce the length and the depth of the effect of the Pinatubo volcano. See my post called “When Eruptions Don’t” for another look at how the climate system responds to a decrease in incoming solar energy due to volcanic eruptions.
I originally published this theory in the journal Energy and Environment. I followed that up with a posting of the same ideas here at Watts Up With That in a post called The Thermostat Hypothesis.
…
Figure 2. Global stratospheric temperatures measured from space.
…