by B.L. Beckman, January 21, 2020 in Mashable/Nature
They were once abundant, in our hairsprays, bug sprays, and refrigerators. And then scientists figured out these substances ripped a hole in the ozone layer, leading to a 1987 plan to phase them out that over time would be agreed to by every country in the world.
More than three decades later, researchers have made a new discovery.
Ozone-depleting substances do more than just gnaw at Earth’s protective layer. They’re also greenhouse gases, so they contribute to the planet’s overall warming by trapping heat, too. And now we may know just how much these substances have contributed to Arctic warming, thanks to a study published in the science journal Nature on Monday.
Between 1955 and 2005, ozone-depleting gases caused half of Arctic climate change (and a third of overall global warming), the study finds. This is primarily due to their heat-trapping qualities, not their ozone munching. The Arctic has seen rapidly melting sea ice for years and is warming faster than the rest of the world.
…
by Jacob Dubé, May 23, 2019 in National Post
Scientists found that between 40 and 60 per cent of the total global CFC-11 emissions originated from eastern China
A chemical banned around the globe for the last 30 years has made an unfortunate resurgence. And all signs, in a new study, point to China as the culprit.
In the 1980s, countries came together to sign The Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, a landmark treaty designed to halt and reduce the production of chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), chemicals used in fridges and foams that had the side effect of tearing through the Earth’s ozone layer.
…
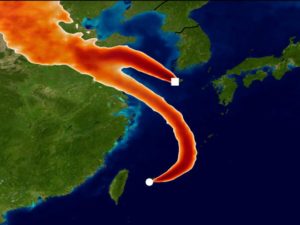
In this graphic, monitoring stations in Japan and Korea designed to track unwanted emissions in the atmosphere attempt to pinpoint the origin of an increase in CFC-11 emissions. Tracking the gas’ presence and weather conditions, scientists concluded it originated from eastern mainland China. A new study published May 22, 2019, found that 40 to 60 per cent of global CFC-11 emissions originated from the region. UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL
La géologie, une science plus que passionnante … et diverse

