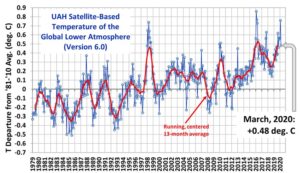
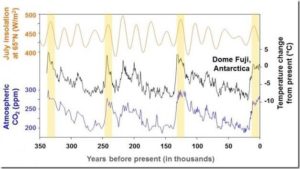
by University of Washington, March 24, 2020 in ScienceDaily
A container ship leaves a trail of white clouds in its wake that can linger in the air for hours. This puffy line is not just exhaust from the engine, but a change in the clouds that’s caused by small airborne particles of pollution.
New research led by the University of Washington is the first to measure this phenomenon’s effect over years and at a regional scale. Satellite data over a shipping lane in the south Atlantic show that the ships modify clouds to block an additional 2 Watts of solar energy, on average, from reaching each square meter of ocean surface near the shipping lane.
The result implies that globally, cloud changes caused by particles from all forms of industrial pollution block 1 Watt of solar energy per square meter of Earth’s surface, masking almost a third of the present-day warming from greenhouse gases. The open-access study was published March 24 in AGU Advances, a journal of the American Geophysical Union.
…