by K. Richard, Oct 19, 2020 in NoTricksZone
Highly anomalous terrain (an active volcano), 40 years of cooling temperatures, and a CO2 record that dramatically contrasts with fluctuating values from forests and meadows reaching 600-900 ppm all beg the question: Is Mauna Loa’s CO2 record globally representative?
Mauna Loa is the Earth’s largest land volcano. It has erupted over 3 dozen times since 1843, making this terrestrial landscape extremely unusual relative to the rest of the globe’s terrain. (Forests, in contrast, cover over 30% of the Earth’s land surface.)
Mauna Loa has been thought to be the world’s best location to monitor global CO2 levels since 1958.
While Mauna Loa CO2 levels show a rise of 338 ppm to 415 ppm since 1980, Mauna Loa temperatures (HCN) show a cooling trend during this same time period. The only warming period in the last 65 years occurred between about 1975 and 1985.
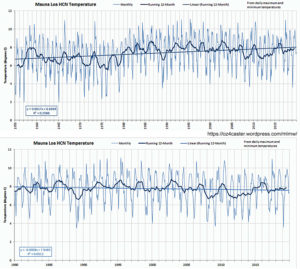
Image Source: oz4caster
Forest CO2 fluctuations
As mentioned above, forests are orders of magnitude more terrestrially representative than the highly anomalous site of the Earth’s largest volcano.
In forests or tree-covered areas, CO2 rises from around 300 ppm in the warmth of the afternoon (~3 p.m.) to over 600 ppm before sunrise (~4 a.m.), when it is cooler (Fennici, 1986, Hamacher et al., 1994). This massive fluctuation occurs daily and CO2 values average out to be far higher than the Mauna Loa record suggests.
