by A. Watts, May 06, 2025 in ClimateChangeDispatch

In a recent editorial published by Phys.org, researchers claim that climate change is driving more powerful and frequent hurricanes, which in turn are causing widespread school closures, labeling it an “overlooked consequence” of our supposedly worsening climate. [emphasis, links added]
This narrative is false.
The available data shows no trend of increasing hurricane frequency or intensity due to human-induced climate change, and if the storms themselves aren’t worsening, the claim that they are causing more missed school days due to climate change collapses under its own weight.
The central claim that hurricanes are becoming more destructive and frequent due to climate change is contradicted by both long-term observational data and the official position of major scientific institutions.
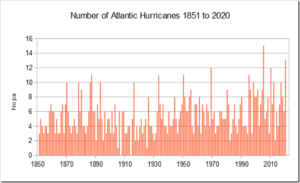
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory (GFDL), there is no strong evidence of an increase in either the number or intensity of hurricanes globally due to human-caused climate change.
…