by D. Archibald, Feb 2, 2022 in WentwothReport
Reports from the current Northern Hemisphere winter include plenty of low temperature records broken, frozen seas off Greece, etc., suggesting that the world is cooling. A correspondent in Missouri writes:
Nearly 800 chill hours here so far … cold forecast for the next 2 weeks. Will hit 1000 easily. The average when we moved here not quite 20 years ago was 5-600 … for the entire winter. (Chill hours refer to the total amount of time a fruit tree needs to be exposed to cold winter temperatures to allow them break dormancy so they will flower and set fruit normally.)
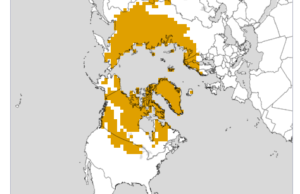
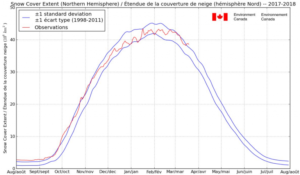
So that is good news for Missouri — they will now be able to grow things like peaches with a high chill hour requirement for fruiting. Confirmation of colder Northern Hemisphere winters is provided by the snow mass trend by the Finnish Meteorlogical Institute:
…
…