by P. Gosselin, Sep 26, 2020 in NoTricksZone
Today, according to government scientists, CO2 is supposed to be the dominant climate driver, overwhelming all the other power natural forces such as solar variability and oceanic cycles.
Map (right): JMA
Yet when we compare (untampered) datasets, we often find surprising parallels and underlying correlations with these now ignored natural factors, which tell us CO2 isn’t what the activists want us to believe it is and that things are really much messier than the simplistic CO2-temperature correlation.
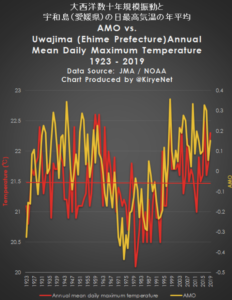
Today we look at a plot of the annual mean daily maximum temperature from Uwajima, Japan, together with the plot of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) going back almost 100 years.
Data: data.jma.go.jp/ / psl.noaa.gov/
Of course, nothing in a complex system like climate is going to show a perfect correlation, yet the above general fit is quite remarkable, which thus suggests regions are climatically interconnected in many yet to be understood ways. Such things aren’t accidental.
In summary: climate science is far from being understood, let alone settled. Anyone suggesting otherwise is likely just trying to sell you a bridge in Brooklyn – or they simply don’t know much about the subject and only parroting media sound bites.