by J. Hunt, Apr 30, 2022 in TheGreatWhite Con
…
There’s a few things to note at first glance. The ice floe continued to decrease in thickness into November. It’s thickness then started to increase, but is currently still less than 2 meters. Also the snow depth has gradually been increasing, and (apart from some data glitches!) is now ~38 cm. Finally, for the moment at least, the ice surface temperature has been slowly warming since mid February and is now ~-11 °C.
…
by P. Gosselin, Apr 30, 2022 in NoTricksZone
New studies on the Atlantic current system assess the threshold between natural fluctuations and a climate change-driven evolution
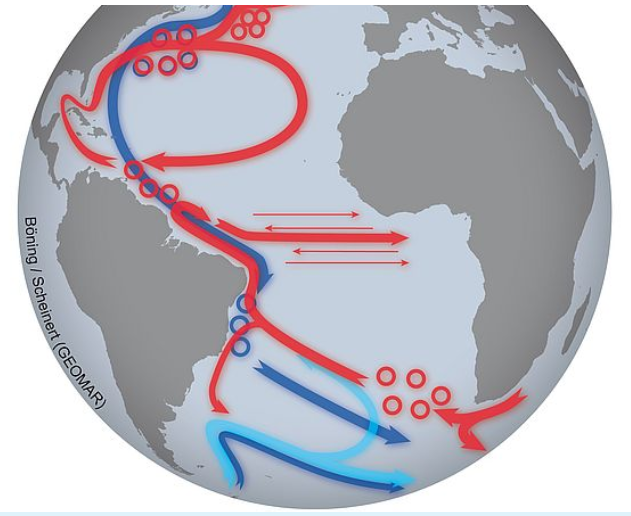
25 April, 2022/Kiel, Germany. With a new publication in the scientific journal Nature Climate Change, researchers from Kiel once again contribute to the understanding of changes in the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) – also known as the “Gulf Stream System”. It is important both for the global climate as well as for climate events in Europe. The authors focus on the question whether human-induced climate change is already slowing down this oceanic circulation. According to the new study, natural variations are still dominant. Improved observation systems could help detect human influences on the current system at an early stage.
Is the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) slowing down? Is this system of ocean currents, which is so important for our climate, likely to come to a halt in the future? Are the observed variations a natural phenomenon or are they already caused by human-induced climate change? Researchers from various scientific disciplines use a wide range of methods to better understand the gigantic oceanic circulation.
“The AMOC provides Europe with a mild climate and determines seasonal rainfall patterns in many countries around the Atlantic. If it weakens over the long term, this will also affect our weather and climate. Other consequences could be a faster rise in sea levels at some coasts or a reduction in the ocean’s ability to take up carbon dioxide and mitigate climate change”, Professor Dr. Mojib Latif, Head of the Research Unit: Marine Meteorology at GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, explains. “We depend on the AMOC in many ways – but so far, we can only guess how it will develop, and whether and how strongly we humans ourselves will push it towards a tipping point where an unstoppable collapse will take its course.”
Using observational data, statistical analyses and model calculations, a team led by Professor Latif has therefore examined changes in the current system over the past one hundred years in greater detail. The results have now been published in the scientific journal Nature Climate Change. According to the researchers, part of the North Atlantic is cooling – a striking contrast to the majority of ocean regions. All evaluations indicate that since the beginning of the 20th century, natural fluctuations have been the primary reason for this cooling. Nonetheless, the studies indicate that the AMOC has started to slow down in recent decades.
…
…
La géologie, une science plus que passionnante … et diverse

