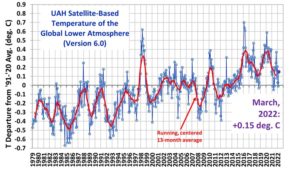
by P. Homewood, Mar 31, 2022 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
solutions and products automatically come to the fore, without the need for subsidies, regulations and mandates.
If renewable energy is all that is promised, it will do the same.
There is of course no doubt that the cheap, abundant and reliable energy provided by fossil fuels has transformed society and made all of us better off than ever before in so many ways.
We get rid of them at our peril!
So far, our transition to renewable energy in the UK has been painfully slow and extremely expensive. Wind and solar power still supply only 3% of the UK’s total energy consumption after two decades of trying. Meanwhile, according to the Office for Budget Responsibility, subsidies for renewables were expected to cost £12 billion in 2021/22. This actually understates the reality because it does not include all of the indirect costs involved in grid balancing and so on, meaning the true cost is probably over £15 billion.
It is of course true that the recent rocketing of gas prices has reset the agenda. But it is important to note that the current price does not reflect the cost of extracting gas. It is the result of an imbalance in supply and demand. Such imbalances have occurred before, and a normally functioning market would quickly increase gas production, driving prices back down to historic levels.
But even before those price rises, it was being claimed that wind and solar power were cheaper than fossil fuel. However such claims fail to take into account the additional system costs imposed by their intermittency.
Moreover, claims that offshore wind costs are now down to around £40/MWh simply are not supported by the evidence. The claims are derived from the prices agreed for Contracts for Difference, the government subsidy mechanism. However, wind farms are under no legal obligation to actually take up these contracts; they are effectively only options.
…