As he points out in the article:
Australia is the world’s most fire-prone continent. In 1900, 11 per cent of its surface burned annually. These days, 5 per cent of the country burns every year. By the end of the century, if we do not stop climate change, higher temperatures and an increase in aridity will likely mean a 0.7 percentage point increase in burnt area, an increase from 5.3 per cent of Australia to 6 per cent.
Unfortunately, many reports on Australia’s fires have exploited the carnage to push a specific agenda, resting on three ideas: that bushfires are worse than ever, that this is caused by global warming, and that the only solution is for political leaders to make even bigger carbon-cut promises.
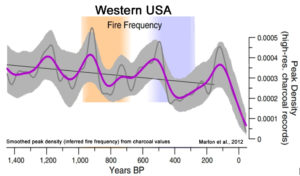
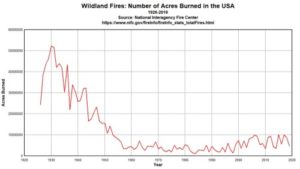
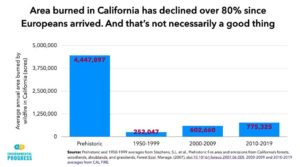
Globally, bushfires burn less land than it used to. Since 1900, global burnt area has reduced by more than one-third because of agriculture, fire suppression and forest management. In the satellite era, NASA and other groups document significant decreases.
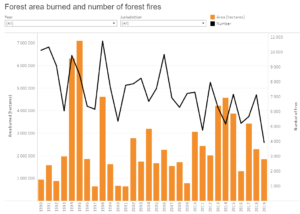
Surprisingly, this decrease is even true for Australia. Satellites show that from 1997 to 2018 the burnt area declined by one-third. Australia’s current fire season has seen less area burned than in previous years. Up to January 26, bushfires burned 19.4 million hectares in Australia — about half the average burn over the similar timeframe of 37 million hectares in the satellite record. (Actually the satellites show 46 million hectares burnt, but 9 million hectares are likely from prescribed burns.)
When the media suggests Australia’s fires are “unprecedented in scale”, it is wrong. Australia’s burnt area declined by more than a third from 1900 to 2000, and has declined across the satellite period. This fire season, at the time of writing, 2.5 per cent of Australia’s area has burned compared with the past 10 years’ 4.8 per cent average by this point.
What is different this year is that fires have been mostly in NSW and Victoria. These are important states with a little more than half the country’s population — and many of its media outlets.
But suggesting fires are caused by global warming rests on cherrypicking these two regions with more fire and ignoring the remaining 87 per cent of Australia’s landmass, where burned area has declined.
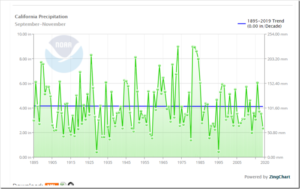
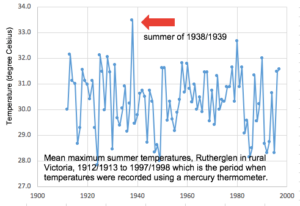
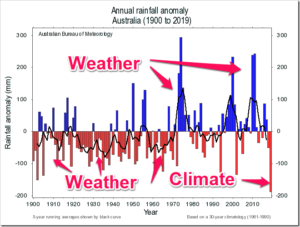
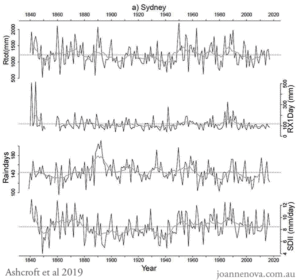
I certainly would take issue with the claim aridity will increase, as we know that rainfall has generally been greater since the 1970s than before.
Lomborg goes on to make the points I have made regularly, that there are many practical ways to reduce the risk of severe fires, and that even if Australia went totally net zero, it would have no effect whatsoever on their climate.
Well worth a read though.