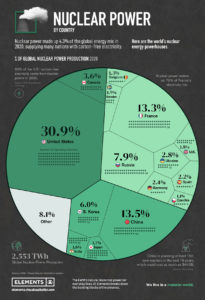
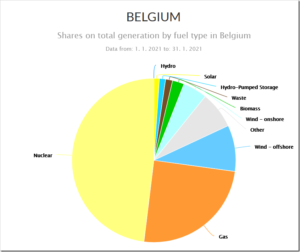
by Bjorn Lomborg, Mar 7, 2022 in ClimateChangeDispatch
The devastating Russian invasion of Ukraine has captured global attention. While the world’s focus is rightly on the human toll and suffering, the crisis has highlighted the need to end reliance on Russian oil and gas. [bold, links added]
To achieve that ambition, we must be pragmatic and invest in sensible alternatives, not engage in wishful thinking about renewable energy.
Every single day, the world spends more than a billion dollarson fossil fuels from Russia, according to Bloomberg reporting.
As Ukrainian Foreign Affairs Minister Dmytro Kuleba tweeted, that money is now paying for the “murder of Ukrainian men, women, and children.” We must end this reliance.
However, this has proved to be easier said than done: Over dozens of years, the world has exchanged trillions of dollars for fossil fuels from the Soviet Union and now from Russia. Our continued use of Kremlin-backed oil and gas reveals two inconvenient truths.
First, reliable energy maintains the foundation of modern society and few are willing to give up its benefits. Access to cheap, abundant, and dependable energy has been the cornerstone of the industrial revolution and humanity’s achievements.
…
…