Le monde regorge de pétrole grâce au développement de la technologie. C’est elle qui est le vecteur de la marche du monde de l’énergie.
Je vous avoue que je ne suis pas le cours du pétrole tous les jours. Cela n’a d’importance que pour les traders et les spéculateurs qui engrangent des bénéfices plantureux en jouant sur quelques centimes de volumes gigantesques.
Si vous voulez comprendre la géopolitique du pétrole et donc de l’énergie , il faut observer les tendances lourdes, comme celle du week-end dernier.
Lorsque j’ai publié en mars 2014 un livre intitulé Vive les énergies fossiles qui indique qu’il n’y a aucune raison objective ou technologique pour que le prix du brut dépasse les 100 dollars le baril, on m’a pris pour un farfelu. Même si j’étais probablement le seul à oser le dire ouvertement en milieu francophone, nombreux étaient ceux qui l’affirmaient de vive voix et par écrit dans le monde. Les faits nous ont donné raison.
LA DEMANDE DE PÉTROLE EN CHUTE LIBRE
Face à la chute brusque de l’activité économique occasionnée par l’épidémie de coronavirus, la demande de pétrole est en chute libre. La consommation chinoise de pétrole a chuté de plus de 3 millions de barils par jour.
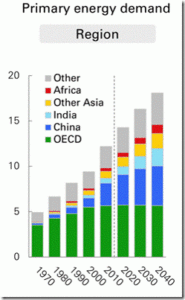
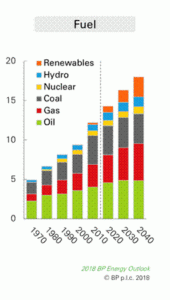
De toute évidence, cette crise sera bien plus profonde pour l’économie mondiale que celle déclenchée par les subprimes en 2008. On s’attend à un net recul de la demande en énergie primaire et singulièrement du pétrole.
Cela va de soi : les avions qui ne volent pas, les voitures qui restent au garage, les restaurants désertés, les stades fermés, les vacances annulées font dégringoler la consommation de produits pétroliers et partant, de toute l’économie. De quoi réjouir les écologistes profonds !
Vendredi dernier à Vienne, à la réunion de l’OPEP, comme d’habitude la Russie – non membre – a été conviée à participer aux travaux. L’OPEP, qui manipule le prix du brut depuis 1973 voulait réduire sa production pour maintenir le prix au niveau précédant l’arrivée sur scène du virus dévastateur. Par la même occasion Ryad aurait mis l’Iran encore plus à genoux pour le peu de pétrole que celui-ci parvient à écouler au marché noir (l’Iran ne sait plus où stocker le pétrole pompé qu’il ne peut pas vendre).
LES ORIGINES DE LA CHUTE DU PRIX DU PÉTROLE BRUT
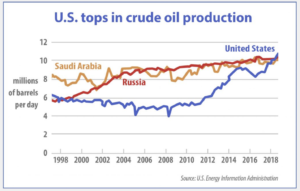
Il est vrai que depuis trois ans, l’OPEP et la Russie se sont accordés pour ajuster leurs extractions à la demande mondiale. Il y a bien eu une tentative de faire chuter le prix de manière à restreindre le développement du pétrole de roche-mère des USA, mais en vain.
Cette fois, Moscou n’a pas voulu suivre le leader de l’OPEP – Ryad – et a refusé d’adhérer à la réduction de la production pour soutenir le prix. L’Arabie Saoudite, piquée au vif, a réagi de manière inverse et a déclaré son intention de porter sa production de brut à plus de 10 millions de barils par jour en avril, après l’expiration de l’accord actuel entre l’OPEP et la Russie fin mars – connu sous le nom d’OPEP+.
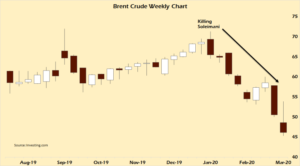
De plus, elle a réduit le prix de tous ses bruts vers toutes les destinations de 6 à 8 dollars le baril. La conséquence ne s’est pas fait attendre : le prix du brut a chuté à environ 32 dollars le baril.
Les contrats à terme sur le pétrole ont subi leur plus grosse perte quotidienne depuis 1991 lors de la guerre du Golfe. Lors de la crise asiatique de 1998, le Financial Times du 10 septembre 1998 titrait que la seule chose qui était plus basse que le cours du pétrole était le moral de l’économie. On pourrait dire la même chose aujourd’hui.
LE MONDE REGORGE DE PÉTROLE GRÂCE À LA TECHNOLOGIE