by P. Homewood, March 21, 2020 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
Bullet Point Summary:
- Coral thrive in warm water, not cold water.
- Recent warming has allowed coral to expand their range poleward, while still thriving near the equator.
- Coral has existed continuously for the past 40 million years, surviving temperatures and carbon dioxide levels significantly higher than what is occurring today.
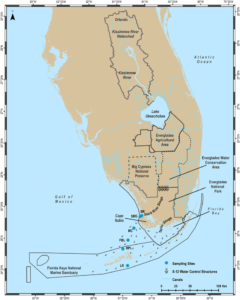
- The primary causes of coral bleaching include oxybenzone (a chemical found in sunscreen), sediment runoff from nearby coastal lands, and cold temperatures like those recorded in 2010 off the Florida coast.
Short Summary: Coral require warm water, not cold water, to live. Coral cannot live outside of tropical or subtropical waters. (See Figure 1.) As Earth continues to modestly warm, coral are extending their range toward the poles while still thriving at and near the equator. The primary reasons for bleaching events include sediment pollution from nearby coastal lands, chemicals found in sunscreen, and cold temperature events. Coral have existed continuously for the past 40 million years. Coral survived and thrived when temperatures were significantly warmer than they are today.
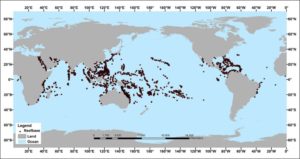
Figure 1: Coral Reef Locations
Continuer la lecture de Climate At A Glance Factchecks–Coral Reefs