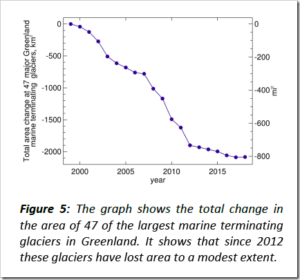
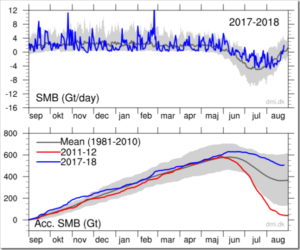
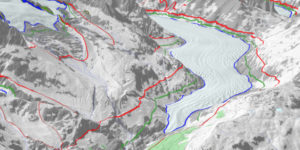
by H.J. Lüdecke & K.E. Puls, January 25, 2020 in NoTricksZone
Prof. Gernot Patzelt is an internationally renowned glaciologist with numerous publications and lectures. Now he has, as it were, presented his life’s work with the book “Gletscher: Klimazeugen von der Eiszeit bis zur Gegenwart“ (Glaciers: Climate Witnesses from the Ice Age to the Present” (Hatje Cantz-Verlag, Berlin, 2019, 266 pages). It combines the overwhelming artistic aesthetics of Alpine glaciers in painting with scientific glaciology.

Gernot Patzelt, Professor of High Altitude Research at the University of Innsbruck and Head of the Alpine Research Centre Obergurgl in Tyrol, was not and is not retired after his retirement in 2004. His lectures, especially those at EIKE climate conferences (here, here) and his writings, which are listed here, bear witness to this. He was also co-author of the book “A. Fischer und G. Patzelt: Gletscher im Wandel: 125 Jahre Gletscher-Meßdienst des Alpenvereins, Springer, 2018″.
His book “Klimazeugen von der Eiszeit bis zur Gegenwart” (Climate Witnesses from the Ice Age to the Present), which is discussed here, breaks new ground by making the otherwise rarely attempted connection between natural aesthetics and scientific description. The Austrian glaciologist has convincingly succeeded in this attempt, namely the connection of painting history with Ice Age history, glacier history, landscape history, vegetation history, climate history, cultural history … and more!
…