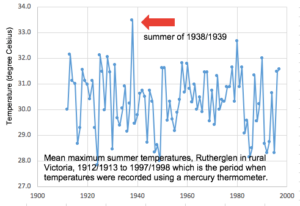
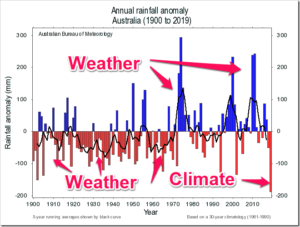
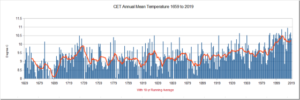
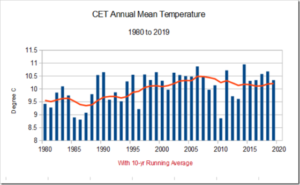
by Tim Ball, September 13, 2018 in Technocracy.News
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) claim of human-caused global warming (AGW) is built on the assumption that an increase in atmospheric CO2 causes an increase in global temperature. The IPCC claim is what science calls a theory, a hypothesis, or in simple English, a speculation. Every theory is based on a set of assumptions. The standard scientific method is to challenge the theory by trying to disprove it. Karl Popper wrote about this approach in a 1963 article, Science as Falsification. Douglas Yates said,
“No scientific theory achieves public acceptance until it has been thoroughly discredited.”
Thomas Huxley made a similar observation.
“The improver of natural knowledge absolutely refuses to acknowledge authority, as such. For him, skepticism is the highest of duties; blind faith the one unpardonable sin.”
In other words, all scientists must be skeptics, which makes a mockery out of the charge that those who questioned AGW, were global warming skeptics. Michael Shermer provides a likely explanation for the effectiveness of the charge.
“Scientists are skeptics. It’s unfortunate that the word ‘skeptic’ has taken on other connotations in the culture involving nihilism and cynicism. Really, in its pure and original meaning, it’s just thoughtful inquiry.”
The scientific method was not used with the AGW theory. In fact, the exact opposite occurred, they tried to prove the theory. It is a treadmill guaranteed to make you misread, misrepresent, misuse and selectively choose data and evidence. This is precisely what the IPCC did and continued to do.
…
…