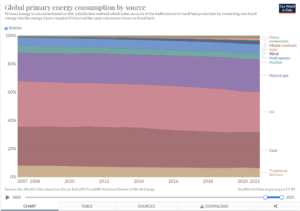
by Our Word Data, Nov 18, 2022
by A. Cang, Nov 15, 2022 in Bloomberg
China’s plans to add to its world-leading fleet of coal power plants are a short-term Band-Aid to address energy security concerns and don’t represent a shift in emissions policies, according to members of the team representing the nation at the COP27 summit.
New plants are being planned to address a spate of high-profile electricity shortages in recent years while providing a buffer to global energy markets that have become more volatile following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, according to interviews with three of China’s delegates at the climate meeting in Egypt.
In the long run, electricity market reforms and massive investments in renewable power and energy storage will eventually curb and curtail coal use, allowing the country to hit its targets of peaking emissions by 2030 and zeroing them out by 2060, they said.
…
by P. Gosselin, Nov 15, 2022 in NoTricksZone
Germany’s Blackout News here reports that not only is Germany’s energy supply faltering profoundly, but so is its wind industry as well, reporting that it is “sliding into a crisis”.
Gloomy outlook also for Germany’s wind energy industry. Photo by P. Gosselin
Wind energy is supposed to step in and play a key role in supplying Germany with energy as other sources get cut off. But that too is not going to plan.
“Nordex is closing its plant in Rostock, Siemens Gamesa is sliding deep into the red and at Vestas the workforce is on strike,” reports Blackout News.
…
by Global Witness, Sept 1, 2022
Hydrogen could be an important part of the renewable energy transition, but not if the fossil fuel industry has its way.
At first glance, hydrogen seems to be the perfect solution to our energy needs. It doesn’t produce any carbon dioxide when used. It can store energy for long periods of time. It doesn’t leave behind hazardous waste materials, like nuclear does. And it doesn’t require large swathes of land to be flooded, like hydroelectricity.
All in all, hydrogen seems too good to be true. No wonder the energy industry is currently pushing hydrogen as the fuel of the future. So…what’s the catch?
Not all hydrogen is created equal
While it’s true that hydrogen is carbon-free at the point of use, this only tells part of the story. Before we get to the stage where hydrogen is used, it first needs to be produced. And it’s this process where the complications begin.
There are several different ways of producing hydrogen, with varying levels of carbon intensity. One is to pass an electric current through water, splitting the water molecules apart into their constituent hydrogen and oxygen atoms. With this method, the key is what kind of electricity you’re using to create the electric current. If the electricity is from renewable sources, then the overall process will be effectively carbon free. If you’re using electricity generated by burning fossil fuels, then the hydrogen will be very carbon intensive.
by M. Champion and S. El Wardany, Oct 23, 2022 in Bloomberg
…
As Egypt prepares to stage COP27, the geopolitical context that shapes all international diplomacy has gone from tense to precarious. The war in Ukraine has divided nations over what some saw as a fight between Russian and Western interests, and supercharged an energy crisis that risks shredding COP26’s most concrete achievement: a global consensus to cut down on coal.
As COP26 approached, falling prices for renewable energy seemed to have forced a reckoning for the dirtiest of fossil fuels. The final text of the summit included calls for a “phasedown” of coal power from any plant that doesn’t capture its carbon and an end to “inefficient” subsidies for fossil fuel. A year later, rampant energy price inflation has combined with a protracted energy crunch to revive demand for coal and put subsidies for fuel of any kind back on political agendas.
“COP27 is to be convened while the international community is facing a financial and debt crisis, an energy-prices crisis, a food crisis, and on top of them the climate crises,” says Egyptian Foreign Affairs Minister Sameh Shoukry, who’s also the conference’s president. “In light of the current geopolitical situation, it seems that transition will take longer than anticipated.”
…
by D. Middleton, Oct 4, 2022 in WUWT
SEPTEMBER 30, 2022
Advances in technology led to record new well productivity in the Permian Basin in 2021The Permian Basin in western Texas and eastern New Mexico is one of the world’s most prolific unconventional oil- and natural gas-producing regions. The Permian Basin has become more productive because of the technological advancements in drilling and completion techniques, which allow operators to economically extract hydrocarbons from the low permeability reservoirs.
The stacked reservoirs of the Permian Basin, and the Delaware and Midland subbasins within it, vary in thickness and depth. Improved geological understanding, known as subsurface delineation, helps operators place wells to optimize well spacing in the most productive areas.
The Permian Basin has produced oil and associated natural gas from vertical wells for decades. Since 2010, advances in hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling led to rapid production growth. The number of new horizontal wells increased to 4,524 in 2021, compared with 350 in 2010. In June 2022, the Permian Basin accounted for about 43% of U.S. crude oil production and 17% of U.S. natural gas production (measured as gross withdrawals).
The length of a well’s horizontal section, or lateral, is a key factor in well productivity. In the Permian Basin, average well horizontal length has increased to more than 10,000 feet in the first nine months of 2022, compared with less than 4,000 feet in 2010.
…
…
See also:
by B. Hart, Sep 13, 2022 in Intelligencer
Since debuting on Substack in the spring of 2021, Doomberg — an anonymous group of writers whose avatar is a distinctive green chicken — has become one of the most popular financial publications on the site. The team has also become a prominent and distinctive voice on finance Twitter (a.k.a. FinTwit). Doomberg’s writers, who come from the world of commodities and heavy industry, deliver deeply informed, often withering analysis that focuses largely on energy policy, their area of expertise. Befitting the site’s name, they often take a darker (or perhaps just more realistic) view than many mainstream sources. Doomberg has been particularly bearish — and prescient — about the unfolding energy crisis in Europe, warning for months that the decision by European leaders to cut off Vladimir Putin from their markets after his invasion of Ukraine risked causing an economic crisis. I spoke via Zoom with one of the Doomberg writers (as represented by that green chicken) about how Russia’s oil industry has thrived despite sanctions, where Europe’s energy squeeze is headed, and why his site is, despite appearances, fundamentally optimistic.
…
by C. Rotter, Sep 20, 2022 in WUWT
Ronald Stein, P.E. is an engineer and Founder of PTS Advance, drawing upon decades of project management and business development experiences. He is an internationally published columnist, energy expert, and Pulitzer Prize nominated author who writes frequently about all aspects of energy and economics and is a Policy Advisor for The Heartland Institute.
…
More about Stein: https://www.heartland.org/about-us/wh…
Stein’s website: https://energyliteracy.net/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/PTSFounder
—
Tom Nelson’s Twitter: https://twitter.com/tan123
Substack: https://tomn.substack.com/
About Tom: https://tomnelson.blogspot.com/2022/0…
Notes for climate skeptics:
https://tomnelson.blogspot.com/2019/0…
ClimateGate emails:
https://tomnelson.blogspot.com/p/clim…
by WJS Editorial Board, Sep 13, 2022 in ClimateChangeDispatch
An unspoken truth of the climate-change crusade is this: Anything the U.S. does to reduce emissions won’t matter much to global temperatures.
U.S. cuts will be swamped by the increases in India, Africa, and especially China. Look no further than China’s boom in new coal-fired electricity.
Under the nonbinding 2015 Paris climate agreement, China can increase its emissions until 2030. And is it ever. [bold, links added]
Between 2015 and 2021, China’s emissions increased by some 11%, according to the Climate Action Tracker, which evaluates nationally determined contributions under the Paris agreement.
The U.S. has reduced its emissions by some 6% between 2015 and 2021. Beijing made minimal new commitments at last year’s Glasgow confab on climate, despite world pressure.
S&P Global Commodity Insights recently estimated that China is planning or building coal-fired power plants with a total capacity of at least 100 gigawatts. Those are merely the projects whose development status is confirmed, so the real number is almost certainly higher.
The total U.S. power capacity is some 1,147 gigawatts. One gigawatt is enough energy to power as many as 770,000 homes.
The nonprofit Global Energy Monitor tracks coal-fired power projects worldwide of 30 megawatts or more, including those planned for the long-term.
It estimates that, as of July 2022, China had some 258 coal-fired power stations—or some 515 individual units—proposed, permitted, or under construction. If completed, they would generate some 290 gigawatts, more than 60% of the world’s total coal capacity under development.
Global Energy Monitor also reports that as of July China had 174 new coal mines or coal-mine expansions proposed, permitted, or under construction that when complete would produce 596 million metric tonnes per year.
…
by B. Ziesloft, Aug 19, 2022 in DailyWire
Strategic Petroleum Reserve levels have reached their lowest levels in four decades as autumn and winter weather conditions approach, according to data from the Energy Information Administration.
President Joe Biden has responded to rising gas prices by releasing one million barrels of oil per day from the Strategic Petroleum Reserves — a stock of emergency crude oil created to “reduce the impact of disruptions in supplies of petroleum products.” Though reserves in January 2021 were as high as 638 million barrels, reserves have fallen to 461 million barrels as of August 2022 — a level not seen since March.
The national average price of gasoline was $2.38 per gallon when President Joe Biden assumed office, according to the Energy Information Administration, and increased to $3.53 per gallon by the start of the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Prices surpassed $5.00 per gallon in early June before subsiding to $3.92 per gallon as of Friday, according to AAA.
Biden nixed an expansion of the Keystone XL Pipeline upon his entrance into office. Yet the commander-in-chief has repeatedly cast the actions of Russian President Vladimir Putin as the main factor behind soaring energy costs.
“Putin’s Price Hike hit hard in May here and around the world: high gas prices at the pump, energy, and food prices accounted for around half of the monthly price increases, and gas pump prices are up by $2 a gallon in many places since Russian troops began to threaten Ukraine,” Biden said in a June statement. “Even as we continue our work to defend freedom in Ukraine, we must do more — and quickly — to get prices down here in the United States.”
…
by P. Homewood, Aug 10, 2022 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
No, the energy crisis is not some unforeseeable consequence of the Ukrainian war. It is the result of years of wishful thinking, preening and short-termism. We sit on 300 years’ supply of coal. We have rich pockets of gas trapped in rocks beneath Central Scotland, Yorkshire, Lancashire and Sussex. We have as good a claim as any country to have invented civil nuclear power. Yet, incredibly, we face blackouts and energy rationing.
The calamity into which we are heading this winter represents a failure of policy under successive governments going back decades. The fact that much of Europe is in the same boat – and that poor Germany is barely in the boat at all, but is clinging by its fingertips to the gunwales – is no consolation.
Like their counterparts in other Western countries, our leaders are now scrambling to make up for past errors. More nuclear power-stations are mooted. The ban on shale gas extraction is reviewed. Sudden attention is paid to potential new sources of clean fuel, from hydrogen to fusion. All good stuff. All too late.
You can’t build a nuclear power plant in less than five years. Even fracking takes around ten months to come online – and that assumes that you have first cleared all the planning hurdles. Hydrogen has vast potential, and what Britain is doing with fusion, not least at the Atomic Energy Authority’s facility in Culham, is mind-blowing. We may well be less than two decades away from solving all our energy problems. But none of that will see us through next winter, when average household fuel bills are set to rise to over £4000.
How did we allow ourselves to become so vulnerable? It was hardly as if disruption in global energy markets was unthinkable. Most of the world’s hydrocarbons are buried under countries with nasty governments. For every Alberta, there are a dozen Irans; for every Norway, a dozen Nigerias. There is even a theory, first advanced by Juan Pablo Pérez Alfonzo, the Venezuelan energy minister who founded OPEC, that the very fact of having oil turns a country into a dysfunctional dictatorship.
We have seen wars, blockades and revolutions across petro-dollar economies. We knew that a break in supply was always a possibility. And it was hardly as if Vladimir Putin was disguising the nature of his regime, for heaven’s sake.
No, we are in this mess because, for most of the twenty-first century, we have ignored economic reality in pursuit of theatrical decarbonisation. Actually, no, that understates our foolishness. Decarbonisation will happen eventually, as alternative energy sources become cheaper than fossil fuels. It is proper for governments to seek to speed that process up. But this goes well beyond emitting less CO2. Our intellectual and cultural leaders – TV producers, novelists, bishops, the lot – see fuel consumption itself as a problem. What they want is not green growth, but less growth.
…
…
by I. Slav, Jul 03, 2022 in OilPrice
There is a glaring problem in the energy transition that not many people are acknowledging.
It is being built on the back of finite resources, and the mining industry is already warning that there aren’t enough metals for all the batteries the transition will require.
Because of the short supply, prices are on the rise, as are prices across commodity sectors.
The energy transition has been set by politicians as the only way forward for human civilization. Not every country on the planet is on board with it, but those that are have the loudest voices. And even amid the fossil fuel crunch that is beginning to cripple economies, the transition remains a goal. It is no secret that the transition—at the scale its architects and most fervent proponents envisage it—would require massive amounts of metals and minerals. What does not get talked about so much is that most of these metals and minerals are already in short supply. And this is only the start of the transition problems.
Mining industry executives have been warning that there is not enough copper, lithium, cobalt, or nickel for all the EV batteries that the transition would require. And they have not been the only ones, either. Even so, the European Union just this month went ahead and effectively banned the sales of cars with internal combustion engines from 2035.
“Rare earth materials are fundamental building blocks and their applications are very wide across modern life,” a senior VP at MP Minerals, a rare-earth miner, told Fortune this month. He added that “one third of the demand in 2035 is not projected to be satisfied based on investments that are happening now.”
Because of the short supply, prices are on the rise, as are prices across commodity sectors. According to a calculation by Barron’s, the price of a basket of EV battery metals that the service tracks has jumped by 50 percent over the past year as a result of various factors, including Western sanctions against Russia, which is a major supplier of such metals to Europe.
…
by Reuters, AP, AFP, July 2022 in DW
European Parliament backs listing nuclear energy, gas as ‘green’
The push to label natural gas and nuclear energy as “green” in order to lure in more private investors was met with heavy resistance. But EU lawmakers ultimately gave it the green light.
The European Parliament on Wednesday voted in favor of a proposal regarding labeling natural gas and nuclear power plants as climate-friendly investments.
The European Commission released the proposal, formally called the EU taxonomy, in December as a list of economic activities that investors can label and market as green in the EU.
A motion to block the proposal received 278 votes in favor and 328 against, while 33 lawmakers abstained.
Unless 20 of the EU’s 27 member states oppose the proposal, it will be passed into law.
…
by J. MCEVOY, Jul 1, 202 in CimateChangeDispatch
World leaders at the G7 summit in Germany signaled they will turn back to fossil fuels despite their commitments to a green energy transition thanks to the ongoing energy crisis.
The war in Ukraine is heavily restricting fuel imports, with Russia cutting off European access to the Nord Stream pipeline and the US imposing a fuel embargo on Putin. [bold, links added]
As a result, the U.S. and European countries are abandoning their climate agenda to return to fossil fuels.
Amid skyrocketing fuel prices, the Biden administration has been forced to abandon certain planks of its climate agenda.
Biden called for a temporary increase in domestic fuel production two weeks ago and also asked Congress to suspend the federal per-gallon gas tax for three months last week.
“The G7 leaders are pretending that nothing has happened to the green agenda,” Benny Peiser, director of the Global Warming Policy Forum, told The Daily Caller News Foundation. “In reality, if you look at individual member states… it’s quite obvious that the green agenda will be sunk.”
…
by BP, June 2022
Energy developments
- Primary energy demand increased by 5.8% in 2021, exceeding 2019 levels by 1.3%.
- Between 2019 and 2021, renewable energy increased by over 8EJ. Consumption of fossil fuels was broadly unchanged.
Fossil fuels accounted for 82% of primary energy use last year, down from 83% in 2019 and 85% five years ago.
…
Egalement: Energie : retour aux réalités
by P. Caddle, Jun 28, 2022 in Breibart
After a warning from the head of three power companies, France’s government has announced that it will restart a coal-fired plant this winter.
A coal-fueled power plant in the north-east of France is due to be restarted by the country’s government this winter in order to better combat energy insecurity resulting in part due to ongoing hostilities with Russia.
The announcement that the Saint-Avold will be brought back online comes shortly after the heads of three major energy companies in France warned that the general public must “immediately” cut back on energy use to better enable officials to better handle energy insecurity.
According to broadcaster RTL, officials have said that the coal-fired plant is being brought back into service “a precaution, given the Ukrainian situation”.
Le Figaro meanwhile notes officials as saying that they will be including so-called “environmental compensation” as part of the plan to reactivate the plant, with the publication claiming that an environmentally neutral reopening for the plant has been demanded by government.
by Bloomberg, June 25, 2022 in Climate Depot
Germany is pushing for Group of Seven nations to walk back a commitment that would halt the financing of overseas fossil fuel projects by the end of the year, according to people familiar with the matter. That would be a major reversal on tackling climate change as Russia’s war in Ukraine upends access to energy supplies.
A draft text shared with Bloomberg would see the G-7 “acknowledge that publicly supported investment in the gas sector is necessary as a temporary response to the current energy crisis.”
The caveat in the proposal is that such funding is done “in a manner consistent with our climate objectives and without creating lock-in effects.”
The text remains under debate and could change before G-7 leaders hold their summit in the Bavarian Alps starting Sunday hosted by Chancellor Olaf Scholz. The UK opposes the proposal, two of the people said. A German government spokesman declined to comment.
EU Leaders Brace for Hard Winter as Russia Tightens Gas Grip
A person familiar with the discussions said Italy wasn’t actively opposing the German proposal. Italy, like Germany, is highly dependent on Russian gas. On Friday, speaking during a press conference in Brussels, Prime Minister Mario Draghi said Italy has managed to reduce Russian gas imports from 40% last year to 25% at the moment. This has been possible also by signing new gas deals in countries including Congo, Algeria and Angola.
…
Germany has responded to the cuts by reviving coal plants and providing financing to secure gas supplies, while continuing with plans to phase out nuclear energy. The World Nuclear Association, an industry lobby group, is urging the G-7 to boost access to nuclear technologies.
by J. Tirone, May 27, 2022 in BNN.Bloomberg
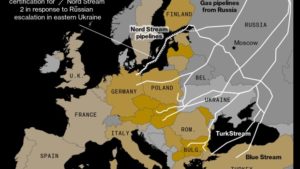
BC-Central-Europe’s-Huge-Gas-Depot-Risks-Being-Empty-Next-Winter , RAG AG
(Bloomberg) — Conflict between Russia and Germany risks leaving one of central Europe’s biggest natural gas depots empty next winter, just as the continent urgently needs to ensure supplies due to the war in Ukraine.
The Haidach underground depot — located in Austria but connected only to the German grid — is unlikely to get filled after Moscow cut supplies to a Gazprom PJSC unit seized by Berlin’s government, according to energy officials in Vienna, who asked not to be identified in exchange for discussing sensitive topics. The depot is equivalent to about a quarter of Austrian storage capacity.
Europeans need to build fuel inventories to keep warm and run their industries next winter. But Russian sanctions on Gazprom Germania GmbH — in retaliation for Berlin seizing the unit earlier this year — are depriving Haidach of crucial supplies needed for energy security should the war in Ukraine disrupt gas transit to the continent.
To make matters worse, Austrian efforts to break the German bottleneck and stash gas at the site is plagued by pipeline constraints. The Alpine country would need to find a way to connect Haidach to the Austrian network and the nation’s grid operator said it’s still studying how it could meet the government’s demand.
“From a technical perspective, a connection between the storage facility and the Penta West pipeline would have to be built,” operator Gas Connect said in emailed response to Bloomberg questions.
Austria’s Penta West is the closest pipeline that could be extended to connect Haidach with the rest of Austria’s 900-kilometer (559-mile) network. Receiving the necessary regulatory and environmental permissions for that could take years, one official said. Even if all approvals were granted, the Penta West pipeline’s capacity is already fully booked by traders fueling west European markets.
A second gas tender being prepared in Vienna, which could be awarded to help fill Haidach with supplies other than Russian, is also facing challenges because there’s no way of verifying where the fuel comes from once it’s been injected into pipelines, a second official said.
…
by The Print, Apr 27, 2022
Beijing [China], April 27 (ANI): Putting the pledges to reach net-zero emissions by 2060 at bay, China is still leading the world in building new coal plants, showed a major annual survey.
Global Energy Monitor’s (GEM) eighth annual survey of the world’s coal plant pipeline on Tuesday reveals that China, the world’s top greenhouse gas polluter, continued to lead all countries in the domestic development of new coal plants, commissioning more new coal capacity in 2021 than the rest of the world combined, reported Straits Times.
Furthering the worries, China’s coal consumption is meant to peak in 2025. China is the world’s largest assembly of coal power plants and this building of new coal plants is posing a critical risk of climate change.
Lauri Myllyvirta, lead analyst for research organisation Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air, which contributed to GEM’s report said, “The power industry’s plan, which appears to have [Chinese] government backing, at least for now, is for coal power capacity to increase until 2030. So new plants are adding more capacity, not just replacing retirements. Last year saw retirements, in fact, slow down.”
By the end of 2021, a total of 176GW of coal capacity was under construction in 20 countries, which is slightly less than in 2020. China represented more than half (52 per cent) of that capacity, and countries in South Asia and Southeast Asia made up a total of 37 per cent.
Flora Champenois from GEM said, “The coal plant pipeline is shrinking, but there is simply no carbon budget left to be building new coal plants. We need to stop, now.”
The report also found that total coal power capacity under development declined 13 per cent last year. Moreover, with the ongoing war in Ukraine, some countries are delaying coal plant retirements as they scramble for energy supplies to keep the lights on.
According to the analysts, this move might temporarily set back global efforts to phase out coal, though soaring coal prices might also prompt some nations to speed up investment in green energy.
Myllyvirta told Straits Times, “The world is experiencing a fossil fuel price shock, leading to overall reduced fossil fuel demand and accelerated plans for clean energy development, reported Straits Times.
“European countries, in particular, have announced very ambitious plans for clean energy and energy efficiency as a part of the effort to end reliance on fossil fuel imports from Russia. These factors will lower coal demand in the coming years,” he added. (ANI)
This report is auto-generated from ANI news service. ThePrint holds no responsibility for its content.
Recommended Content by theprint.in
by A. Epstein, Feb 4, 2022 in EnergyTalkingPoints
A frequent question I get is: “Why do you think you’re right, given that so many experts disagree with you?”
I have two answers to this:
- What most expert researchers think about energy and climate is very different from what we are told they think. (This is the issue, discussed extensively in Fossil Future, of how our “knowledge system” fails to do its job of synthesizing and disseminating expert research.)
- Because, as a humanist philosopher, I consider the full context of facts about fossil fuels from a human flourishing perspective. And most thinkers on energy and climate do not do this. Not even close.
Here are 33 controversial conclusions I have come to, explained thoroughly in Fossil Future, based on full context, pro-human thinking.
If you find any of these conclusions particularly compelling, please share this list with your favorite TV or podcast hosts. I’m happy to discuss any of these topics during the Fossil Futuremedia tour, beginning in April; the book will be released April 19th. (To book me, DM me on Twitter @AlexEpstein.)
….
….
by P. Homewood, Mar 31, 2022 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
solutions and products automatically come to the fore, without the need for subsidies, regulations and mandates.
If renewable energy is all that is promised, it will do the same.
There is of course no doubt that the cheap, abundant and reliable energy provided by fossil fuels has transformed society and made all of us better off than ever before in so many ways.
We get rid of them at our peril!
So far, our transition to renewable energy in the UK has been painfully slow and extremely expensive. Wind and solar power still supply only 3% of the UK’s total energy consumption after two decades of trying. Meanwhile, according to the Office for Budget Responsibility, subsidies for renewables were expected to cost £12 billion in 2021/22. This actually understates the reality because it does not include all of the indirect costs involved in grid balancing and so on, meaning the true cost is probably over £15 billion.
It is of course true that the recent rocketing of gas prices has reset the agenda. But it is important to note that the current price does not reflect the cost of extracting gas. It is the result of an imbalance in supply and demand. Such imbalances have occurred before, and a normally functioning market would quickly increase gas production, driving prices back down to historic levels.
But even before those price rises, it was being claimed that wind and solar power were cheaper than fossil fuel. However such claims fail to take into account the additional system costs imposed by their intermittency.
Moreover, claims that offshore wind costs are now down to around £40/MWh simply are not supported by the evidence. The claims are derived from the prices agreed for Contracts for Difference, the government subsidy mechanism. However, wind farms are under no legal obligation to actually take up these contracts; they are effectively only options.
…
by P. Homewood, Mar 16, 2022 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
The seasons are changing, and for many of us that means it’s time for a spring clean. My back patio has been gathering months’ worth of soil and winter debris, so I now need to blow it up. I will use the same method to clean the grime off my car. After ensuring the area is clear, and any nearby houses or pedestrians are safe, I will subject the car to lots of explosions. In each case, I shall be using a power washer, of the kind that Halfords sells for around 50 quid.
At this point, I expect the pedants among you to start quibbling. The hydraulic pressure from my power washer is not an ‘explosion’, you might point out. Water pressure does not cause ‘a sudden and rapid expansion’, which is how many dictionaries define ‘explosion’. But according to the BBC’s most senior green journalist, environment editor Roger Harrabin, there is no difference between hydraulic pressure and explosions – and Roger’s word is good enough for me.
Harrabin began to deploy the word ‘explosions’ in his reports in 2011, when the UK’s coalition government and the public began to warm to a new and emerging energy resource: shale gas.
Full story here.
by Bloomberg, Mar 15, 2022 in ClimateDepot
China plans a massive increase in coal mining, a move that will dramatically reduce its reliance on imports and deal a blow to its near-term climate actions.
The National Development and Reform Commission, the nation’s top economic planner, told officials from major mining regions at a meeting late last week that it wants to boost domestic production capacity by about 300 million tons, according to people familiar with the matter. It also plans to build a 620 million-ton stockpile of the fuel split between government, miners and users.
Such an increase in output would cut the country’s already scant dependence on foreign imports after global prices hit record levels in the wake of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. The measures also highlight concerns that China’s reliance on fossil fuels remains as entrenched as ever, as it seeks to enhance energy security to limit disruptions to economic growth, regardless of the impact on its climate goals.
It’s hard to overstate the importance to China of coal, the most-polluting fossil fuel. The nation produces and consumes more than half of global supply, and it’s the biggest contributor to its world-leading greenhouse gas emissions. China has said that coal consumption should begin to fall off in the second half of this decade as it strives to peak emissions across the economy by 2030.
The production increase would be split, with 150 million tons of capacity coming from new, upgraded operations and another 150 million from open-pit mines and some mines that had previously been shut. Daily output should average 12.6 million tons, according to the NDRC, which is even higher than the record-breaking levels reached in the fall after shortages caused widespread industrial brownouts.
The NDRC didn’t give a timeline for the ramp-up, but if last year’s all-out push on production is anything to go by, it could happen relatively quickly. The added 300 million tons of capacity is equivalent to China’s typical annual imports. The nation produced over 4 billion tons of its own coal last year.
The new edicts on supply follow other measures intended to guarantee a smoothly running power system, which still relies on coal for about 60% of its needs. The government has ordered mines and power plants to sign medium and long-term contracts for 100% of their generation, and will enforce a price range of between 570 and 770 yuan a ton for those supplies.
by. P. Homewood, Mar 13, 2022 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
This single chart from the US EIA explains just why oil prices are shooting up there:
https://www.eia.gov/petroleum/production/
…
The oil boom initiated by Trump saw crude oil output increase by a half between 2016 and 2019.
Output naturally collapsed in early 2020 as a result of the pandemic, which affected both supply and demand. But since then output has only slowly recovered, and is still 9% below 2019 levels.
It is worth pointing out that demand in 2021 was still not back to 2019 levels. Assuming it recovers this year, it is likely to put further upward pressure on prices, unless production increases as well.
To put the numbers into perspective, the US produces a sixth of the world’s crude oil. The increase US output between 2016 and 2019 was 205 million tonnes, and represents 5% of global output.
Small changes in supply have a disproportionate effect on international oil prices, because demand is so inelastic. An extra 5% on world production would have a significant impact on prices.