by Bloomberg News, November 20, 2019
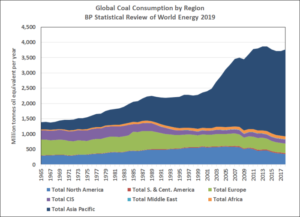
China has enough coal-fired power plants in the pipeline to match the entire capacity of the European Union, driving the expansion in global coal power and confounding the movement against the polluting fossil fuel, according to a report.
The nation has almost 148 gigawatts of coal-fired capacity under active construction or likely to be resumed after being suspended, Global Energy Monitor, a non-profit group that tracks coal stations, said in the report Thursday based on plant-by-plant data. That’s almost equivalent to 150 gigawatts of existing coal fleet capacity in the EU and more than the combined 105 gigawatts under construction in the rest of the world, it said.
In contrast to many other countries, including the U.K.’s pledge to shut all coal plants by 2025, Beijing remains committed to coal as its biggest source of power, representing a major challenge to global emissions reduction targets. Its additions in the 18 months to June dwarf declines elsewhere in the world, according to the report.
…

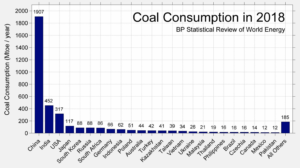
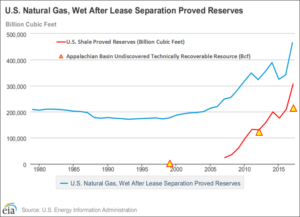 Figure 2. “The effects American ingenuity and new technology can have.”…
Figure 2. “The effects American ingenuity and new technology can have.”…