by Nathalie Sauer, April 30, 2019 in ClimateHomeNews
Mayor unveils plan aiming for 100% zero-emissions vehicles by 2050 amid sweeping climate package for the city
Los Angeles’ car-choked arteries will run clean within decades, according to a green reform package unveiled by mayor Eric Garcetti on Monday.
Speaking only a week after New York City mayor Bill de Blasio announced his own framework climate legislation, Garcetti presented plans to revolutionise local car culture and green the city’s buildings, which together account for three-quarters of LA’s emissions.
“Los Angeles needs to lead, but the whole world needs to act. This plan gives us a fighting chance,” Garcetti told the Los Angeles Times. “It’s sort of a ‘greenprint’ for every other city in the country and the world, hopefully.”
The legislation, which builds upon a previous 2015 sustainability plan, calls on the city to hike its percentage of zero emission vehicles from 1.4% in 2018 to 25% by 2025, 80% by 2035 and 100% by 2050. To do this, the City Town Hall intends to raise its number of publicly available electric-vehicle chargers from 2,100 to 28,000.
…




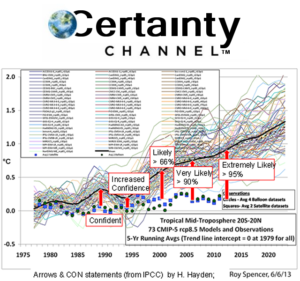






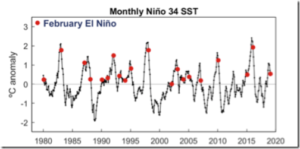

 Average CO2 emissions from new cars rose in 2017 for the first time since 2010 — largely due to the fuel change, according to final data
Average CO2 emissions from new cars rose in 2017 for the first time since 2010 — largely due to the fuel change, according to final data