by Roy Spencer, May 15, 2019 in GWPF
A major uncertainty in figuring out how much of recent warming has been human-caused is knowing how much nature has caused. The IPCC is quite sure that nature is responsible for less than half of the warming since the mid-1900s, but politicians, activists, and various green energy pundits go even further, behaving as if warming is 100% human-caused.
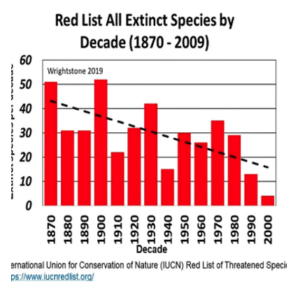
The fact is we really don’t understand the causes of natural climate change on the time scale of an individual lifetime, although theories abound. For example, there is plenty of evidence that the Little Ice Age was real, and so some of the warming over the last 150 years (especially prior to 1940) was natural — but how much?
The answer makes as huge difference to energy policy. If global warming is only 50% as large as is predicted by the IPCC (which would make it only 20% of the problem portrayed by the media and politicians), then the immense cost of renewable energy can be avoided until we have new cost-competitive energy technologies.
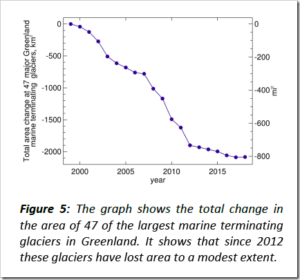
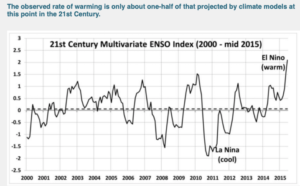
The recently published paper Recent Global Warming as Confirmed by AIRSused 15 years of infrared satellite data to obtain a rather strong global surface warming trend of +0.24 C/decade. Objections have been made to that study by me (e.g. here) and others, not the least of which is the fact that the 2003-2017 period addressed had a record warm El Nino near the end (2015-16), which means the computed warming trend over that period is not entirely human-caused warming.
If we look at the warming over the 19-year period 2000-2018, we see the record El Nino event during 2015-16 (all monthly anomalies are relative to the 2001-2017 average seasonal cycle):
…
See also Spencer’s blog