by Charles the moderator, June3, 2019 in WUWT
The Version 6.0 global average lower tropospheric temperature (LT) anomaly for May, 2019 was +0.32 deg. C, down from the April, 2019 value of +0.44 deg. C:
by Charles the moderator, June3, 2019 in WUWT
The Version 6.0 global average lower tropospheric temperature (LT) anomaly for May, 2019 was +0.32 deg. C, down from the April, 2019 value of +0.44 deg. C:
by Paul Berth, 31 mai 2019 in ScienceClimatEnergie
Selon certaines prédictions, basées sur des modèles informatiques, de nombreux récifs coralliens auront disparu des océans tropicaux au cours des 80 prochaines années[1]. La cause est bien évidemment le réchauffement climatique pouvant provoquer un blanchiment des coraux. Par exemple, en 2014–2017, a eu lieu un évènement global de blanchiment, le 3e au cours des 20 dernières années, et de nombreux coraux furent affectés sur des milliers de kilomètres carrés[2],[3]. Les médias, avides de catastrophisme, en ont beaucoup parlé avec des titres une fois de plus très alarmistes (exemple ici).
Cependant, les choses ne sont pas si simples. Des données satellitaires et des études de terrain ont montré que tous les récifs coralliens ne se comportent pas de la même manière: de nombreux récifs n’ont pas blanchi pendant le dernier épisode El Niño, une très grande partie des coraux a résisté au stress thermique, et de fortes variations locales et régionales ont été observées dans le blanchiment[4]. La relation entre température élevée de l’eau de mer et blanchiment des coraux n’est donc pas évidente. Afin d’éclaircir la situation une équipe américaine a récemment publié une analyse globale des évènements de stress thermique en considérant 3351 sites différents dans 81 pays (Sully et al. 2019, dans Nature Communications[5]). Cette analyse globale est unique et démontre que les coraux sont en train de s’adapter par sélection naturelle et sont désormais un peu plus résistants au blanchiment. Nous avons ici une belle démonstration du fait que les modèles informatiques sont parfois bien loin de la réalité de terrain et qu’il ne faut pas tirer de conclusions toujours hâtives!
…
by Jim Steele, May 17, 2019 in WUWT
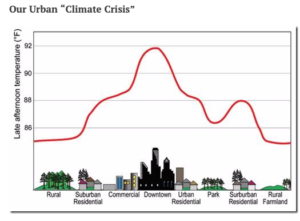
Based on a globally averaged statistic, some scientists and several politicians claim we are facing a climate crisis. Although it’s wise to think globally, organisms are never affected by global averages. Never! Organisms only respond to local conditions. Always! Given that weather stations around the globe only record local conditions, it is important to understand over one third of the earth’s weather stations report a cooling trend (i.e. Fig 4 below ) Cooling trends have various local and regional causes, but clearly, areas with cooling trends are not facing a “warming climate crisis”. Unfortunately, by averaging cooling and warming trends, the local factors affecting varied trends have been obscured.
It is well known as human populations grow, landscapes lose increasing amounts of natural vegetation, experience a loss of soil moisture and are increasingly covered by heat absorbing pavement and structures. All those factors raise temperatures so that a city’s downtown area can be 10°F higher than nearby rural areas. Despite urban areas representing less than 3% of the USA’s land surface, 82% of our weather stations are located in urbanized areas. This prompts critical thinkers to ask, “have warmer urbanized landscapes biased the globally averaged temperature?” (Arctic warming also biases the global average, but that dynamic must await a future article.)
…
by Vijay Jayaraj, May 16,2019 in WUWT
A new temperature reconstruction, using proxy temperature measurements from locations in central Asia, has revealed that there has been no warming in the past 432 years.
The Global Warming “Hiatus” or Pause
The word “hiatus” became popular in recent years after the discovery of a pause or hiatus in global warming. There has been a lack of warming in the atmosphere since 1999, despite the predictions of computer climate models.
…
by Roy Spencer, May 15, 2019 in GWPF
A major uncertainty in figuring out how much of recent warming has been human-caused is knowing how much nature has caused. The IPCC is quite sure that nature is responsible for less than half of the warming since the mid-1900s, but politicians, activists, and various green energy pundits go even further, behaving as if warming is 100% human-caused.
The fact is we really don’t understand the causes of natural climate change on the time scale of an individual lifetime, although theories abound. For example, there is plenty of evidence that the Little Ice Age was real, and so some of the warming over the last 150 years (especially prior to 1940) was natural — but how much?
The answer makes as huge difference to energy policy. If global warming is only 50% as large as is predicted by the IPCC (which would make it only 20% of the problem portrayed by the media and politicians), then the immense cost of renewable energy can be avoided until we have new cost-competitive energy technologies.
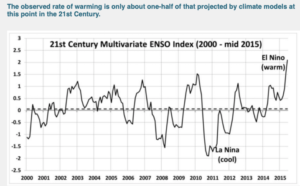
The recently published paper Recent Global Warming as Confirmed by AIRSused 15 years of infrared satellite data to obtain a rather strong global surface warming trend of +0.24 C/decade. Objections have been made to that study by me (e.g. here) and others, not the least of which is the fact that the 2003-2017 period addressed had a record warm El Nino near the end (2015-16), which means the computed warming trend over that period is not entirely human-caused warming.
If we look at the warming over the 19-year period 2000-2018, we see the record El Nino event during 2015-16 (all monthly anomalies are relative to the 2001-2017 average seasonal cycle):
…
See also Spencer’s blog
by P. Gosselin, May11, 2019 in NoTricksZone
April data have been coming in, and they show that warming has been missing at many sub-Arctic stations over the past decades.
…
…
by K. Richard, May 9, 2019 in NoTricksZone
Another new paper published in Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology casts further doubt on the paradigm that says CO2 has historically been a temperature driver.
Evidence from the tropical Atlantic indicates today’s regional temperatures (15.5°C) are 7.5°C colder than a peak temperatures (23°C) between 15,000 to 10,000 years ago, when CO2 hovered around 220 ppm.
…
by P. Homewood, May 6, 2019 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
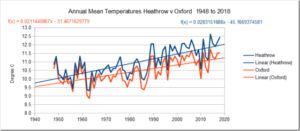
This study aims to estimate the affect of urbanisation on daily maximum and minimum temperatures in the United Kingdom. Urban fractions were calculated for 10 km × 10 km areas surrounding meteorological weather stations. Using robust regression a linear relationship between urban fraction and temperature difference between station measurements and ERA‐Interim reanalysis temperatures was estimated. For an urban fraction of 1.0, the daily minimum 2‐m temperature was estimated to increase by 1.90 ± 0.88 K while the daily maximum temperature was not significantly affected by urbanisation. This result was then applied to the whole United Kingdom with a maximum T min urban heat island intensity (UHII) of about 1.7K in London and with many UK cities having T min UHIIs above one degree.
This paper finds through the method of observation minus reanalysis that urbanisation has significantly increased the daily minimum 2‐m temperature in the United Kingdom by up to 1.70 K.
https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/asl.896
As ever, the real issue with UHI is the change in the effect over time. Has, for instance, the effect of UHI increased in London and other cities increased over the last century, or was it just as great in 1919?
What we do know is that, generally speaking, towns and cities have both expanded over time, and seen increasing development in terms of roads, buildings, traffic and economic activity.
Indeed, these same tendencies also apply in small towns and what may appear to be relatively rural sites.
We also know that many of the sites used by the Met Office in their UK temperature series are urban and airport locations.
…
https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/public/weather/climate-historic/#?tab=climateHistoric
…
by CFACT, May 2nd, 2019
Newly published data gathered by NASA’s AIRS satellite confirm the Earth is warming more slowly than has been forecast by climate activists and the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Data gathered from 2003 through 2017 confirm temperatures remained essentially flat from 2003 through 2015, finally rising briefly as a strong El Nino formed in 2015 and lasted into 2016 (https://ggweather.com/enso/oni.htm). Even with El Nino adding an illusory warming spike at the end of the period, temperatures still rose just over 0.2 degrees during the 15-year period. That pace works out to less than 1.5 degrees of warming per century.
IPCC initial forecasts called for 0.3 degrees Celsius of warming per decade, while skeptic forecasts have tended to hover around 0.1 degrees. As temperatures warmed more slowly than IPCC predicted, IPCC reduced its forecasts to meet skeptics in the middle, moving to a predicted 0.2 degrees warming per decade. Even so, the newly published data indicate IPCC continues to forecast more warming than real-world data indicate.
…
par Jean N., 4 mai 2019 in Science-Climat-Energie
Dans une récente publication[1] de 2019, l’équipe russe de G.A. Zherebtsov présente un mécanisme permettant d’expliquer le réchauffement global. Ce mécanisme, basé sur une série d’observations, ne fait pas intervenir le taux de CO2 atmosphérique mais les rayons cosmiques solaires ainsi que le champ électromagnétique terrestre. Les chercheurs qui ont pensé à ce mécanisme (inconnu du GIEC) font tous partie de l’institut de Physique Terrestre et Solaire de la Branche Sibérienne de l’Académie Russe des Sciences (Irkutsk, Russie). Si le mécanisme de l’équipe de Zherebtsov est correct, on pourrait alors se passer de l’hypothèse de l’effet de serre radiatif qui, comme vous le savez peut-être, pose certains problèmes (voir ici, ici et ici). Le but du présent article est simplement de présenter ce mécanisme et de montrer par la même occasion que la science du climat est loin d’être dite.
1. Observations réalisées le 7 novembre 2004
Les chercheurs russes ont d’abord constaté qu’à certaines latitudes il y a un lien assez fort entre le flux de rayons cosmiques solaires (RCS) et la température de la troposphère. Ceci est par exemple bien visible dans un évènement qui a débuté le 7 novembre 2004 au niveau des hautes latitudes de l’hémisphère nord (55°N-65°N). Ce jour-là, le flux de RCS était particulièrement fort d’environ 3 ordres de grandeur plus élevé par rapport à la normale (Figure 1a). Une tempête géomagnétique s’est ensuite déclarée le jour suivant et a duré au moins 5 jours (il s’agit de fluctuations brusques et intenses du magnétisme terrestre qui proviennent d’une perturbation de l’ionosphère par l’activité solaire). Ceci est bien visible sur le tracé des indices géomagnétiques AE (Figure 1b) et Dst (voir aussi ici), indices obtenus par certaines stations de mesure placées au sol et réparties en divers endroits de la planète (Figure 1c). Il existe de nombreux indices géomagnétiques et il n’est pas nécessaire d’être un spécialiste pour comprendre la suite du présent article. Il faut simplement retenir que le champ magnétique terrestre est perturbé les jours suivant l’arrivée des RCS. Voyons maintenant si tout ceci peut avoir un effet sur la température de la basse troposphère.
…
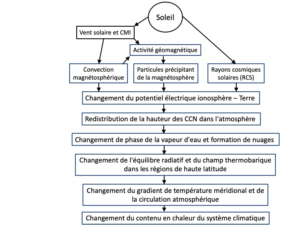
Figure 4. Diagramme présentant le mécanisme de Zherebtsov. Source : Zherebtsov et al. (2019) J Atm Solar Terrestrial Physics 182:217–222 (traduit de l’anglais).
by Drieu Godefridi, 2 mai 2019 in Contrepoints
Réduire le réchauffement global sur Terre de 1,5° ? Dans un récent rapport, le Giec échafaude quatre scénarios pour y parvenir. Mais aucun d’eux ne tient la route.
es quatre scénarios mettent en œuvre à des degrés divers les techniques dites de Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR), qui compensent les émissions humaines de CO2. Écoutons les experts « scientifiques » du GIEC — dont la plupart ne sont pas scientifiques. Lisons les experts du GIEC :
…
by Dr. Roy Spencer, April 30, 2019 in WUWT
I have previously addressed the NASA study that concluded the AIRS satellite temperatures “verified global warming trends“. The AIRS is an infrared temperature sounding instrument on the NASA Aqua satellite, providing data since late 2002 (over 16 years). All results in that study, and presented here, are based upon infrared measurements alone, with no microwave temperature sounder data being used in these products.
That reported study addressed only the surface “skin” temperature measurements, but the AIRS is also used to retrieve temperature profiles throughout the troposphere and stratosphere — that’s 99.9% of the total mass of the atmosphere.
Since AIRS data are also used to retrieve a 2 meter temperature (the traditional surface air temperature measurement height), I was curious why that wasn’t used instead of the surface skin temperature. Also, AIRS allows me to compare to our UAH tropospheric deep-layer temperature products.
So, I downloaded the entire archive of monthly average AIRS temperature retrievals on a 1 deg. lat/lon grid (85 GB of data). I’ve been analyzing those data over various regions (global, tropical, land, ocean). While there are a lot of interesting results I could show, today I’m going to focus just on the United States.
…
by William J. Davis, September 2017, in ResearchGate
Assessing human impacts on climate and biodiversity requires an understanding of the relationship between the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth’s atmosphere and global temperature (T). Here I explore this relationship empirically using comprehensive, recently-compiled databases of stable-isotope proxies from the Phanerozoic Eon (~540 to 0 years before the present) and through complementary modeling using the atmospheric absorption/transmittance code MODTRAN. Atmospheric CO2 concentration is correlated weakly but negatively with linearly-detrended T proxies over the last 425 million years.
…
by Dr Roy Spencer, April 23, 2019 in GlobalWarming
This post has two related parts. The first has to do with the recently published study of AIRS satellite-based surface skin temperature trends. The second is our response to a rather nasty Twitter comment maligning our UAH global temperature dataset that was a response to that study.
…
Furthermore, that period (January 2003 through December 2017) shows significant warming even in our UAH lower tropospheric temperature (LT) data, with a trend 0.01 warmer than the “gold standard” HadCRUT4 surface temperature dataset (all deg. C/decade):
AIRS: +0.24
GISTEMP: +0.22
ECMWF: +0.20
Cowtan & Way: +0.19
UAH LT: +0.18
HadCRUT4: +0.17I’m pretty sure the Susskind et al. paper was meant to prop up Gavin Schmidt’s GISTEMP dataset, which generally shows greater warming trends than the HadCRUT4 dataset that the IPCC tends to favor more. It remains to be seen whether the AIRS skin temperature dataset, with its “clear sky bias”, will be accepted as a way to monitor global temperature trends into the future.
What Satellite Dataset Should We Believe?
…
by P. Homewood, April 24, 2019 in NotaLotOfPeopleKnowThat
The DMI has just published its Greenland Climate Data Collection for last year, and it is worth looking at the temperature data:
There are six stations with long records, Upernavik, Nuuk, Ilulissat, Qaqortoq, Narsarsuaq and Tasilaq.

…
Throughout Greenland we find that temperatures in the last two decades are little different to the 1920s to 60s.
The only exceptions were 2010 on the west coast sites, which was an unusually warm year, and 2016 on the east coast at Tasilaq, another warm year there.
Noticeably, last year was actually colder than the 1981-2010 average at all of the west and south coast stations.
by Jean N., 17 avril 2019 in Science-Climat-Energie
Cet article s’inscrit dans le cadre de l’activité actuelle médiatique tout azimut en Belgique, notamment relayée par les marches hebdomadaires des étudiants pour le climat. Comme vous le savez peut-être si vous êtes un lecteur fidèle de SCE, nous avons démontré dans plusieurs articles que l’hypothèse de l’effet de serre radiatif ne tient pas la route (ici, ici et ici) et n’explique pas le léger réchauffement actuel de la basse atmosphère. Les fins connaisseurs savent également qu’il existe de nombreuses publications scientifiques remettant en cause l’hypothèse de l’effet de serre radiatif (plus de 500 publications rien que pour 2018), toutes écrites par des physiciens, des chimistes, des géologues ou des climatologues. Si cette somme d’évidences vous a convaincu, le GIEC aurait alors tort sur toute la ligne et le CO2 d’origine anthropique n’aurait aucun rôle majeur déterminant la température de la basse troposphère. Cependant, admettons un instant que vous ne soyez pas convaincu et admettons donc que le GIEC ait raison. Tout ce qui est écrit dans son dernier rapport spécial devrait alors être vrai… Quelle serait alors la part de la Belgique dans le réchauffement? Asseyez-vous pour ne pas tomber, vous allez être surpris.
Figure 1. Extrait de la Figure SPM.1 du résumé pour décideurs (SPM) du rapport spécial publié par le GIEC fin 2018. Cette figure se trouve en page 8 du rapport du GIEC.
…
When heavy rain falls over the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia and the eastern Pacific Ocean, it is a good indicator that temperatures in central California will reach 100°F in four to 16 days, according to a collaborative research team from the University of California, Davis, and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Climate Center in Busan, South Korea.
The results were published in Advances in Atmospheric Scienceson April 12.
FROM PREDICTION TO PROTECTION
Heat waves are common in the Central California Valley, a 50-mile-wide oval of land that runs 450 miles from just north of Los Angeles up to Redding. The valley is home to half of the nation’s tree fruit and nut crops, as well as extensive dairy production, and heat waves can wreak havoc on agricultural production. The dairy industry had a heat wave-induced economic loss of about $1 billion in 2006, for instance. The ability to predict heat waves and understand what causes them could inform protective measures against damage.
…
by K. Richard, April 4, 2019 in NoTricksZone
…
by Roy Spencer, April 3, 2019 in GlobalWarming
Summary: The monthly anomalies in Australia-average surface versus satellite deep-layer lower-tropospheric temperatures correlate at 0.70 (with a 0.57 deg. C standard deviation of their difference), increasing to 0.80 correlation (with a 0.48 deg. C standard deviation of their difference) after accounting for precipitation effects on the relationship. The 40-year trends (1979-2019) are similar for the raw anomalies (+0.21 C/decade for Tsfc, +0.18 deg. C for satellite), but if the satellite and rainfall data are used to estimate Tsfc through a regression relationship, the adjusted satellite data then has a reduced trend of +0.15 C/decade. Thus, those who compare the UAH monthly anomalies to the BOM surface temperature anomalies should expect routine disagreements of 0.5 deg. C or more, due to the inherently different nature of surface versus tropospheric temperature measurements.
…
…
Conclusions
The UAH tropospheric temperatures and BOM surface temperatures in Australia are correlated, with similar variability (0.70 correlation).
Accounting for anomalous rainfall conditions increases the correlation to 0.80. The Tsfc trends have a slightly greater warming trend than the tropospheric temperatures, but the reasons for this are unclear. Users of the UAH data should expect monthly differences between the UAH and BOM data of 0.6 deg. C or so on a rather routine basis (after correcting for their different 30-year baselines used for anomalies: BOM uses 1961-1990 and UAH uses 1981-2010).
by Jim Steele, April 4, 2019 in WUWT
Extreme scientists and politicians warn we will suffer catastrophic climate change if the earth’s average temperature rises 2.7°F above the Little Ice Age average. They claim we are in a climate crisis because average temperature has already warmed by 1.5°F since 1850 AD. Guided by climate fear, politicians fund whacky engineering schemes to shade the earth with mirrors or aerosols to lower temperatures. But the cooler Little Ice Age endured a much more disastrous climate.
The Little Ice Age coincides with the pre-industrial period. The Little Ice Age spanned a period from 1300 AD to 1850 AD, but the exact timing varies. It was a time of great droughts, retreating tree lines, and agricultural failures leading to massive global famines and rampant epidemics. Meanwhile advancing glaciers demolished European villages and farms and extensive sea ice blocked harbors and prevented trade.
…
by P. Gosselin, April 3, 2019 in NoTricksZone
Canada’s CBC here recently cited “a leaked report” which claimed Canada is “warming at twice the global rate.”
According to the “leaked report”, Canada’s annual average temperature over land has warmed 1.7 C when looking at the data since 1948. But that claim is misleading when recent data is considered.
Over the past 25 years, since scientists began to warn that the planet was warming in earnest, there has not been any warming when one looks at the untampered data provided by the Japan meteorology Agency (JMA) that were measured by 9 different stations across Canada. These 9 stations have the data dating back to around 1983 or 1986, so I used their datasats.
Looking at the JMA database and plotting the stations with longer term recording, we have the following chart:
…
by P. Homewood, April 3, 2019 in NotaLotofPeopleKnowThat
According to CET, March 2019 was the 17th warmest on record since 1659, 1.2C higher than the 1981-2010 average.
Sound impressed? No, thought not!
The month as a whole actually seemed to be pretty unremarkable. There was some mild weather at the start of the month, accompanied by very wet weather. The last few days were also pleasant and sunny.
But unusually warm?
The graph at the top gives a bit of perspective.
First of all it is obvious that last month was pretty typical of Marchs during the last 30 years or so.
The fact that it is 1.2C above the 30-year average means little, as natural variability means some years are warmer and others cooler, such as last year. That’s what an average is.
Indeed, in the last 30 years, eleven had March anomalies of 1C or more. Six of these years were warmer than this March.
By far the warmest Marchs were in 1957 and 1938, again suggesting that there was nothing unusual about last month.
The other thing which stands out is that most Marchs used to be much colder than normal until the 1980s.
…
https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/hadobs/hadcet/cetmaxdly1878on_urbadj4.dat
see also here (WUWT)
by P. Gosselin, March 31, 2019 in NoTricksZone
By Kirye
and Pierre Gosselin
One fellow climate blogger recently wrote on how he’s been been looking at GHCN ‘unadjusted’ data and noticed that scientists at NASA appear to have been altering them: “This is a fairly disturbing development,” he wrote.
Heating up Reykjavik and Nuuk
Cited as an example is Reykyavik, Iceland. According to Tony Heller here, “The current version V4 has massively cooled the past, to make it look like Iceland is warming.”
Heller then posted a chart showing the difference between v2 unadjusted and the new v4 ‘unadjusted’ for the Reykjavik station.
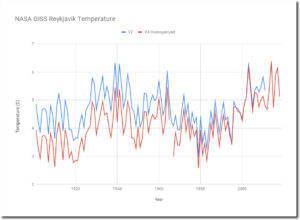
Heller also found here that the same appears to be the case for Nuuk, Greenland as well.
…
by Ian L.M. Goddard & S. Bett, Marcy 21, 2019 in WUWT
Abstract
This study aims to estimate the affect of urbanisation on daily maximum and minimum temperatures in the United Kingdom. Urban fractions were calculated for 10 km × 10 km areas surrounding meteorological weather stations. Using robust regression a linear relationship between urban fraction and temperature difference between station measurements and ERA‐Interim reanalysis temperatures was estimated.
For an urban fraction of 1.0, the daily minimum 2‐m temperature was estimated to increase by 1.90 ± 0.88 K while the daily maximum temperature was not significantly affected by urbanisation. This result was then applied to the whole United Kingdom with a maximum T min urban heat island intensity (UHII) of about 1.7K in London and with many UK cities having T min UHIIs above one degree.
This paper finds through the method of observation minus reanalysis that urbanisation has significantly increased the daily minimum 2‐m temperature in the United Kingdom by up to 1.70 K.
…
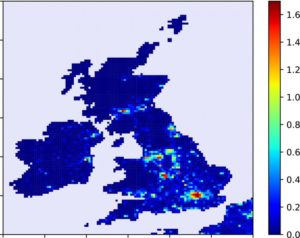
Figure 5 Map showing the change in T min due to the urbanisation at the 10 km × 10 km scale over the United Kingdom and Ireland. The colour bar shows the magnitude of the temperature change in K
by Javier, April 30, 2017 in ClimateEtc.
First in a two part series on Holocene climate variability.
Summary: Holocene climate is characterized by two initial millennia of fast warming followed by four millennia of higher temperatures and humidity, and a progressively accelerating cooling and drying for the past six millennia. These changes are driven by variations in the obliquity of the Earth’s axis. The four millennia of warmer temperatures are called the Holocene Climatic Optimum which was 1-2°C warmer than the Little Ice Age. This climatic optimum was when global glaciers reached their minimum extent. The Mid-Holocene Transition, caused by orbital variations, brought a change in climatic mode, from solar to oceanic dominated forcing. This transition displaced the climatic equator, ended the African Humid Period and increased El Niño activity.
…

Figure 36. Holocene temperature profile. A. Summer (July-August) Central England temperature reconstruction from multiple proxies and sources by H. H. Lamb.Crosses represent dating and temperature uncertainty. Black dots are centennial averages. Red dot is 1900-1965 average. Source: Lamb, H.H. 1977. Climate: Present, past and future. Volume 2. B. Greenland temperature reconstruction based on an average of uplift corrected δ18O isotopic data from Agassiz and Renland ice cores. This average has been corrected for changes in the δ18O of seawater and calibrated to borehole temperature records. Some historical periods are indicated. Source: B. Vinther et al., 2009.
…