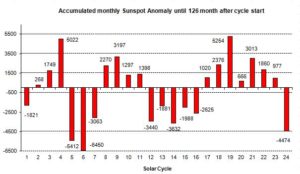
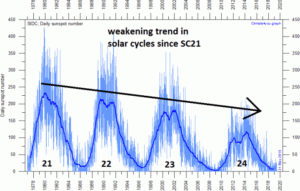
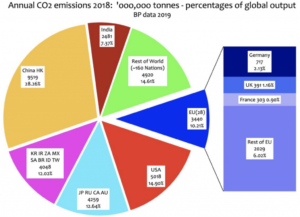
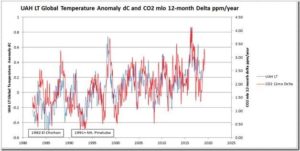
by P. Gosselin, June 25, 2019 in NoTricksZone
By Kirye
and Pierre GosselinIt’s been long known that NASA GISS has been going through its historical temperature data archives and erasing old temperature measurements and replacing them with new, made up figures without any real legitimate reason.
This practice has led to the formation of new datasets called “adjusted” data, with the old datasets being called “V3 unadjusted”. The problem for global warming activists, however, was that when anyone looks at the old “V3 unadjusted” – i.e. untampered data – they often found a downward linear temperature trend. Such negative trends of course are an embarrassment for global warming alarmists, who have been claiming the planet is warming up rapidly.
The adjusted “unadjusted” data
So what to do? Well, it seems that NASA has decided to adjust its “V3 unadjusted datasets” and rename them as “V4 unadjusted”. That’s right, the adjusted data has become the new V4 “unadjusted” data.
And what kind of trend does the new “V4 unadjusted” data show?
You guessed it. The new V4 unadjusted data are now yielding warmed up trends, even at places where a cooling trend once existed.
This is how NASA uses its magic wand of fudging to turn past cooling into (fake) warming.
6 examples of scandalous mischief by NASA
What follows are 6 examples, scattered across the globe and going back decades, which demonstrate this scandalous mischief taking place at NASA.
No. 1
Punta Arenas, Chile. Here we see how a clear cooling trend has been warmed up by NASA to produce a slight cooling trend:
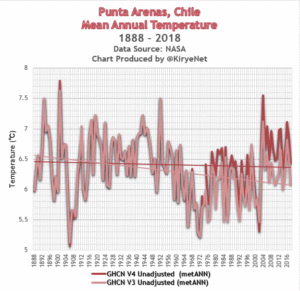
giss.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/gistemp/stdata_show_v3
giss.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/gistemp/stdata_show_v4
…